The Role of Data Governance in Ensuring Data Quality
Data governance lays the groundwork for achieving and maintaining high-quality data. By establishing clear standards, procedures, and controls, it ensures that data remains accurate, consistent, and reliable across an organization. These measures reduce errors and discrepancies, fostering trust in the data and the insights it generates. A robust governance framework addresses challenges like miscommunication and misinterpretation, enabling organizations to make informed decisions. The ingredients of data governance, such as defined roles and accountability, play a pivotal role in safeguarding data integrity and enhancing its value for operational and strategic purposes.
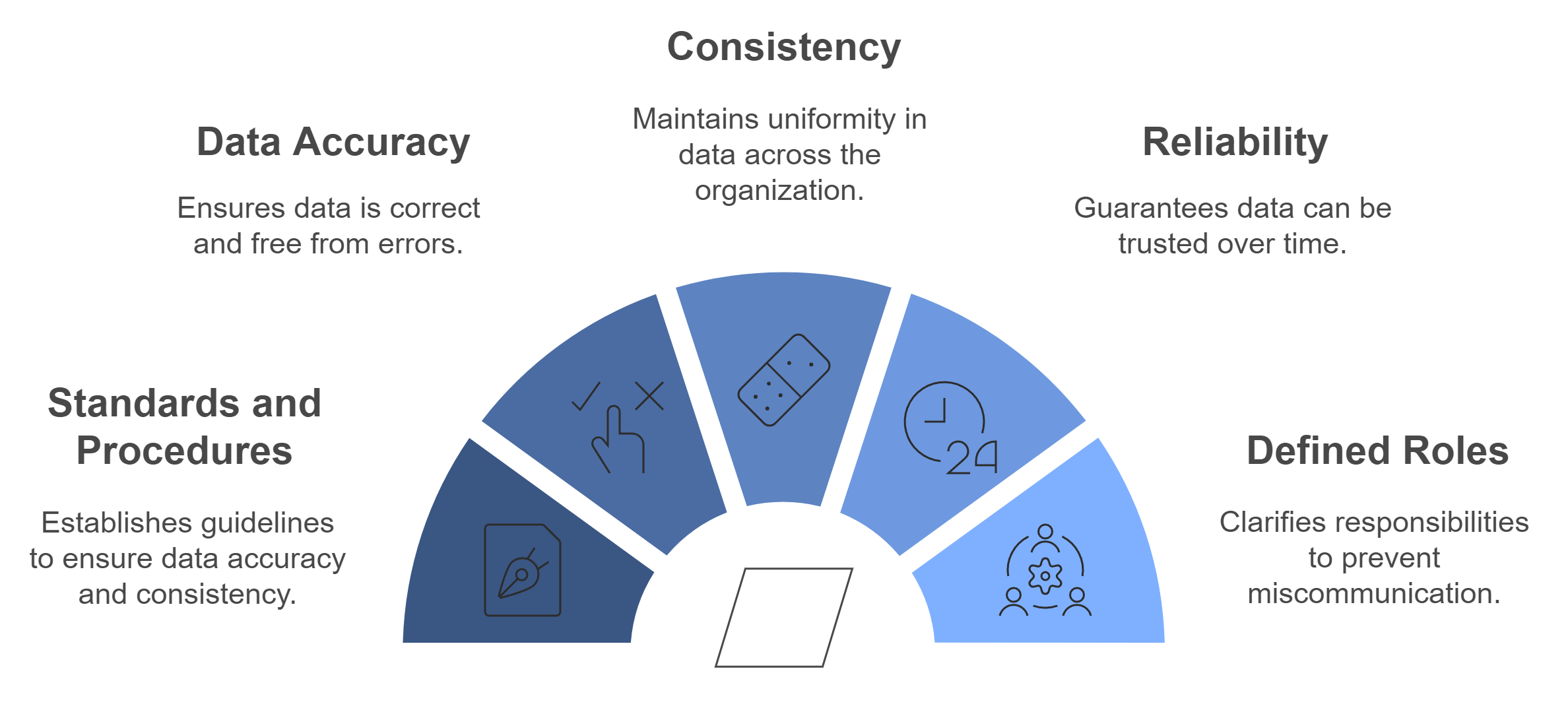
Key Takeaways
Data governance establishes clear standards and procedures that ensure data accuracy, consistency, and reliability across organizations.
Implementing a robust governance framework helps address common data quality challenges, such as data silos and human errors, leading to better decision-making.
Accountability and defined roles within data governance are crucial for maintaining data quality, as they ensure that individuals take responsibility for data management.
Continuous monitoring and regular audits are essential for identifying and resolving data quality issues, fostering a culture of accountability.
Leveraging advanced data quality tools and technologies enhances the effectiveness of governance frameworks, automating processes and reducing human error.
Compliance with legal and regulatory standards is strengthened through data governance, protecting organizations from potential risks and penalties.
A strong culture of data stewardship encourages all employees to prioritize data quality, transforming data into a strategic asset for the organization.
Defining Data Governance and Data Quality
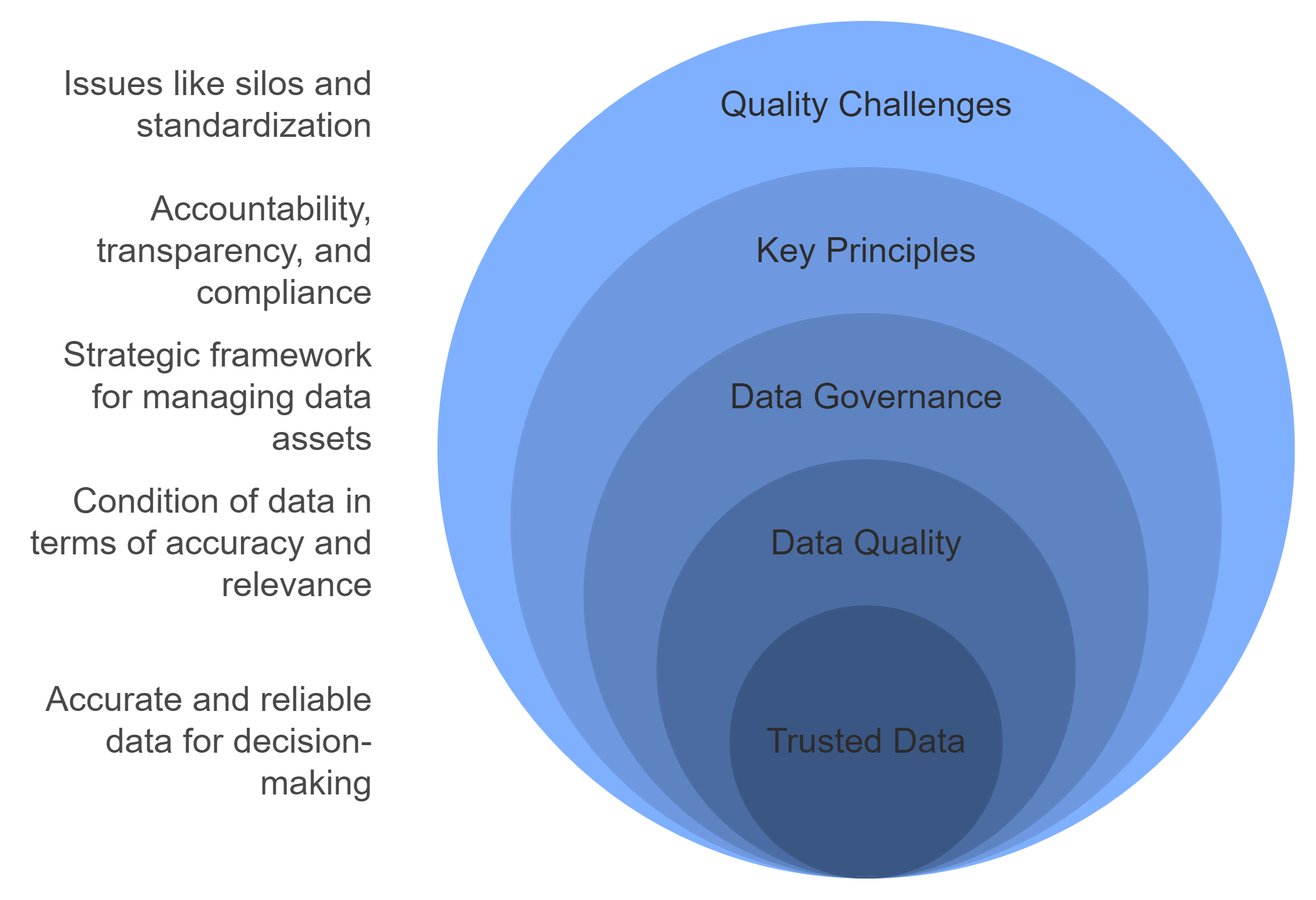
What Is Data Governance?
Data governance refers to the strategic framework that organizations use to manage their data assets effectively. It establishes clear rules, processes, and roles to ensure data is accurate, consistent, and secure throughout its lifecycle. This framework provides a structured approach to handling data from collection to analysis, ensuring it meets organizational standards and regulatory requirements. By implementing data governance, organizations can create a foundation for trusted information, enabling better decision-making and operational efficiency.
Key principles of data governance include accountability, transparency, and compliance. Accountability ensures that specific individuals or teams take responsibility for managing data quality and security. Transparency allows stakeholders to understand how data is collected, stored, and used. Compliance ensures adherence to legal and regulatory standards, reducing risks associated with data breaches or inaccuracies. These principles collectively enhance the value and reliability of data within an organization.
What Is Data Quality?
Data quality refers to the condition of data in terms of its accuracy, completeness, relevance, and reliability. High-quality data serves as a strategic asset, empowering organizations to make informed decisions and achieve better outcomes. Accurate data reflects the real-world scenario it represents, while completeness ensures no critical information is missing. Relevance guarantees that the data aligns with the specific needs of the organization, and reliability ensures consistency across systems and processes.
Organizations often face challenges in maintaining data quality due to issues like data silos, human errors, and lack of standardization. Addressing these challenges requires a proactive approach, including the use of data quality tools and technologies. These tools, when supported by a robust data governance framework, can significantly improve the accuracy and credibility of data. Reliable data enhances organizational performance and builds trust among stakeholders.
The Interdependence Between Data Governance and Data Quality
Data governance and data quality are deeply interconnected. Data governance provides the structure and oversight needed to maintain high data quality. Without governance, data quality initiatives often lack direction and consistency. Governance frameworks define the policies and procedures that guide data management, ensuring data remains accurate, complete, and relevant.
Effective data governance addresses common data quality challenges by unifying practices under a single framework. For example, it reduces fragmentation caused by data silos and enforces standardization across systems. It also assigns clear roles and responsibilities, ensuring accountability for data quality at every level of the organization. By integrating governance with data quality tools, organizations can monitor and improve data continuously.
"Ensuring data quality starts and ends with governance." This statement highlights the pivotal role governance plays in creating a foundation for trusted information. Organizations that prioritize governance not only enhance data quality but also unlock the full potential of their data assets. This synergy between governance and quality drives better decision-making, operational efficiency, and compliance.
Key Dimensions of Data Quality
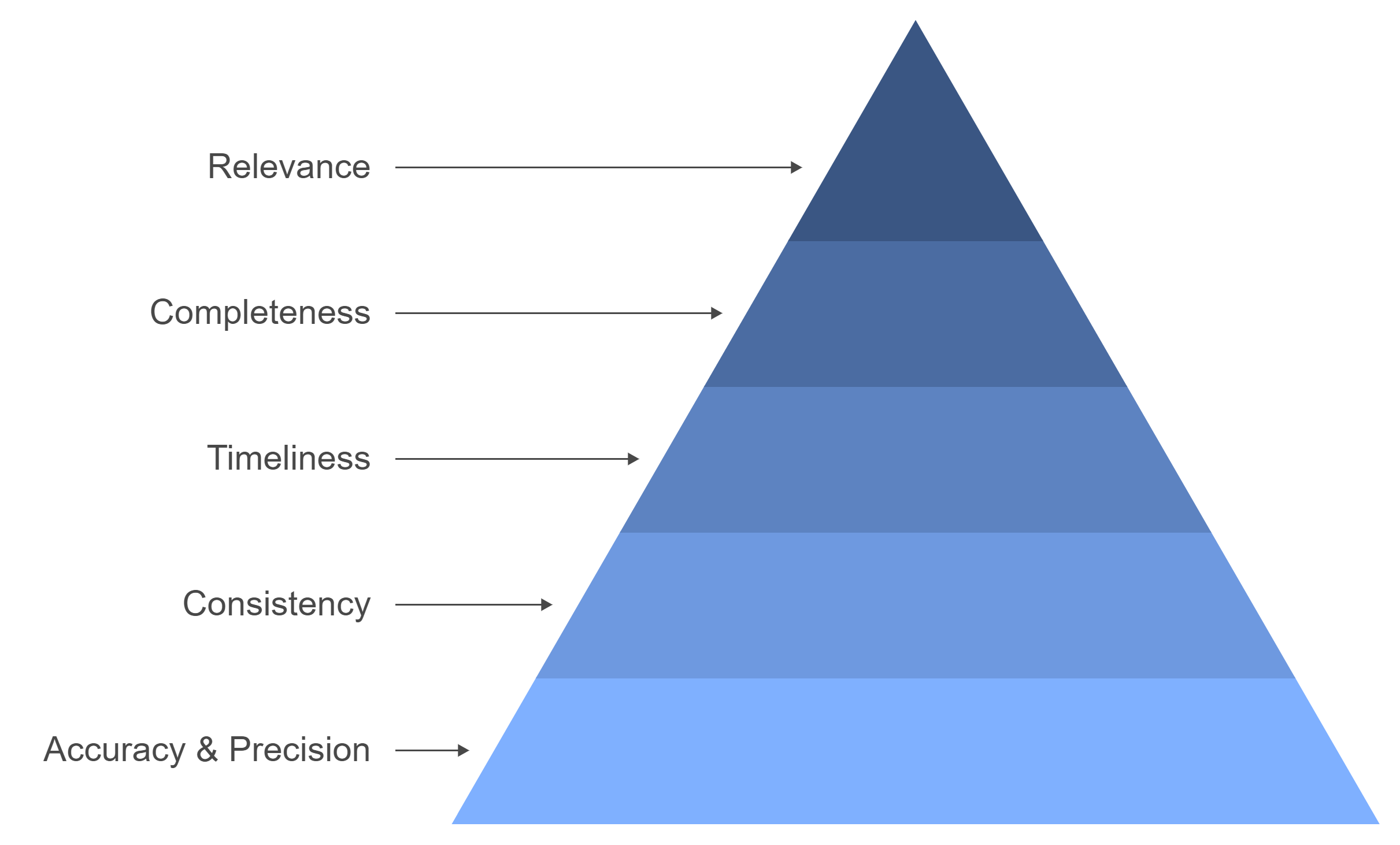
Accuracy and Precision
Accuracy ensures that data reflects real-world scenarios without errors or distortions. Precision, on the other hand, focuses on the level of detail and exactness in the data. Together, these dimensions form the backbone of reliable information. Organizations with strong data governance frameworks achieve higher accuracy and precision by implementing clear standards and controls. These measures reduce errors during data collection, storage, and processing.
For example, a retail company tracking customer purchases must ensure that transaction records are accurate and precise. Errors in pricing or quantities can lead to financial discrepancies and customer dissatisfaction. Data governance frameworks address such issues by enforcing validation rules and monitoring processes. This approach ensures that data remains trustworthy and actionable.
"Accuracy and precision are not optional; they are essential for informed decision-making." This principle underscores the importance of maintaining high standards in data management.
Consistency Across Systems
Consistency ensures that data remains uniform and coherent across different systems and platforms. Inconsistent data can lead to confusion, misinterpretation, and flawed decision-making. Organizations with robust governance frameworks minimize inconsistencies by standardizing data formats, definitions, and processes.
Consider a healthcare organization managing patient records across multiple departments. Without consistency, patient information may vary between systems, leading to errors in diagnosis or treatment. Data governance frameworks address this challenge by establishing unified data standards and ensuring adherence across all systems. This practice enhances operational efficiency and builds trust in the data.
A strong governance framework also reduces fragmentation caused by data silos. By integrating data from various sources into a cohesive system, organizations can ensure consistency and reliability. This integration fosters better collaboration and more accurate insights.
Timeliness and Real-Time Data Needs
Timeliness refers to the availability of data when it is needed, while real-time data needs focus on providing up-to-date information instantly. Both dimensions are critical for organizations operating in fast-paced environments. Data governance frameworks play a vital role in ensuring timely access to accurate and relevant data.
For instance, financial institutions rely on real-time data to monitor market trends and make investment decisions. Delayed or outdated information can result in missed opportunities or financial losses. Governance frameworks address this need by implementing automated data pipelines and monitoring systems. These tools ensure that data remains current and accessible.
Timeliness also impacts decision-making in industries like logistics and supply chain management. Accurate, real-time data enables companies to optimize routes, manage inventory, and respond to disruptions effectively. By prioritizing timeliness, organizations can enhance their agility and competitiveness.
"In the digital age, timely data is as valuable as accurate data." This statement highlights the growing importance of real-time information in driving success.
Completeness and Avoiding Missing Data
Completeness ensures that all necessary data is present and accounted for within a dataset. Missing or incomplete data can lead to flawed analyses, inaccurate conclusions, and poor decision-making. Organizations must prioritize completeness to maintain the integrity of their data and the reliability of their insights.
A strong data governance framework plays a critical role in achieving completeness. It establishes clear standards for data collection and storage, ensuring that no critical information is overlooked. For instance, in customer relationship management (CRM) systems, missing contact details or transaction histories can hinder effective communication and service delivery. Governance frameworks address this by enforcing mandatory fields and validation checks during data entry.
"Incomplete data is like an unfinished puzzle—it leaves gaps that compromise the bigger picture." This analogy emphasizes the importance of completeness in creating a reliable foundation for analysis.
Organizations with robust governance frameworks also implement regular audits to identify and address gaps in their datasets. These audits help maintain data integrity and ensure that all relevant information is captured. By prioritizing completeness, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and build trust in their data-driven processes.
Relevance for Decision-Making
Relevance ensures that data aligns with the specific needs and objectives of an organization. Irrelevant or outdated data can mislead decision-makers and waste valuable resources. High-quality data must be tailored to support strategic goals and provide actionable insights.
Data governance frameworks enhance relevance by defining clear criteria for data collection and usage. They ensure that only pertinent information is gathered, reducing clutter and improving focus. For example, in marketing campaigns, collecting data on customer preferences and purchasing behavior proves more valuable than gathering unrelated demographic details. Governance frameworks streamline this process by aligning data collection efforts with organizational priorities.
"Relevant data transforms information into actionable insights." This statement highlights the power of relevance in driving informed decisions.
Organizations with effective governance frameworks also implement processes to regularly review and update their datasets. This ensures that the data remains aligned with evolving business needs and market conditions. By focusing on relevance, businesses can make better decisions, optimize their strategies, and achieve their objectives more efficiently.
Common Challenges in Maintaining Data Quality
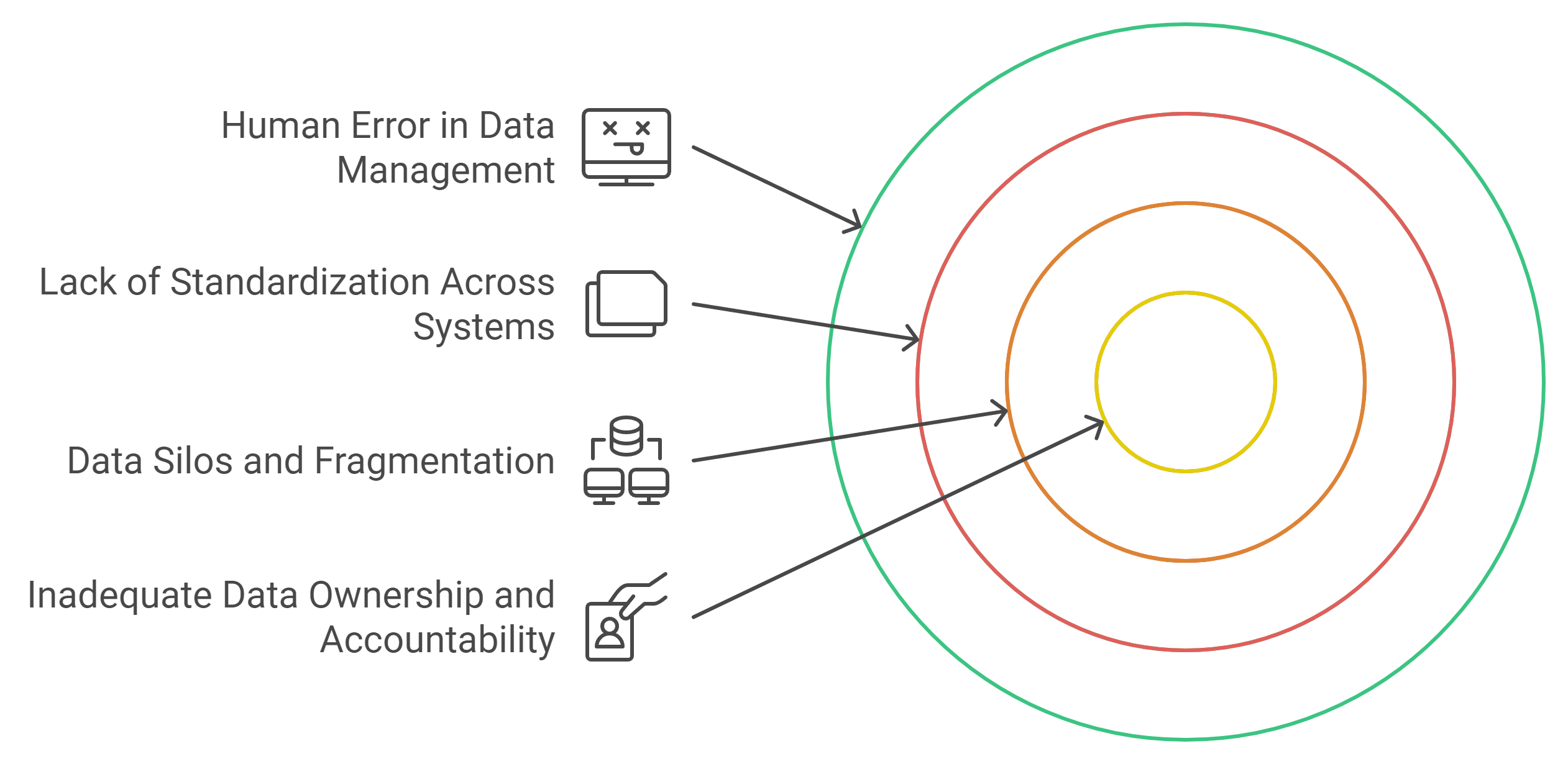
Data Silos and Fragmentation
Data silos occur when information is isolated within specific departments or systems, preventing seamless integration across an organization. This fragmentation creates barriers to achieving a unified view of data, leading to inconsistencies and inefficiencies. For instance, a company’s sales team might store customer data in one system, while the marketing team uses another. These disconnected systems can result in duplicated or conflicting information.
To address this challenge, organizations must prioritize breaking down silos. Centralized data repositories or integrated platforms can unify disparate datasets. Data governance frameworks play a critical role by establishing protocols for data sharing and integration. These measures ensure that all departments access consistent and reliable information, fostering collaboration and improving decision-making.
"Data silos hinder progress by isolating valuable information. Breaking them down unlocks the full potential of organizational data."
Lack of Standardization Across Systems
Inconsistent data formats and definitions across systems create significant challenges for maintaining data quality. Without standardization, organizations struggle to align data from various sources, leading to errors and misinterpretations. For example, one system might record dates in the format MM/DD/YYYY, while another uses DD/MM/YYYY. Such discrepancies can cause confusion and inaccuracies during analysis.
Standardization ensures uniformity in how data is collected, stored, and processed. Organizations can achieve this by implementing clear data standards and guidelines. Data governance frameworks enforce these standards, ensuring compliance across all systems. Regular audits and validation checks further enhance consistency, reducing the risk of errors.
"Standardization transforms fragmented data into a cohesive and reliable resource for decision-making."
Human Error in Data Management
Human error remains one of the most common causes of data quality issues. Mistakes during data entry, processing, or analysis can compromise accuracy and reliability. For instance, a simple typo in a customer’s email address can disrupt communication and impact service delivery. Errors like these accumulate over time, creating significant challenges for organizations.
Minimizing human error requires a combination of training, automation, and governance. Employees must receive proper training on data management practices to reduce mistakes. Automated tools, such as data validation software, can identify and correct errors in real time. Data governance frameworks establish accountability by defining roles and responsibilities, ensuring that individuals take ownership of data quality.
"Human error is inevitable, but robust governance and automation can mitigate its impact on data quality."
By addressing these challenges, organizations can build a strong foundation for maintaining high-quality data. Data governance frameworks provide the structure and oversight needed to overcome obstacles like silos, lack of standardization, and human error. These efforts ensure that data remains accurate, consistent, and reliable, enabling better decision-making and operational success.
Inadequate Data Ownership and Accountability
Inadequate data ownership and accountability often lead to significant challenges in maintaining data quality. When organizations fail to assign clear responsibilities for managing data, errors and inconsistencies can proliferate. Without designated individuals or teams overseeing data processes, it becomes difficult to ensure accuracy, completeness, and reliability.
Data ownership involves assigning specific roles to individuals or departments responsible for managing and safeguarding data. Accountability ensures that these stakeholders take ownership of their tasks and address any issues that arise. Organizations lacking these structures often experience fragmented data management, where no one takes responsibility for errors or discrepancies. This lack of accountability creates gaps in data quality and undermines trust in the information.
"Accountability is the cornerstone of effective data management." This principle highlights the importance of assigning clear roles to maintain high-quality data.
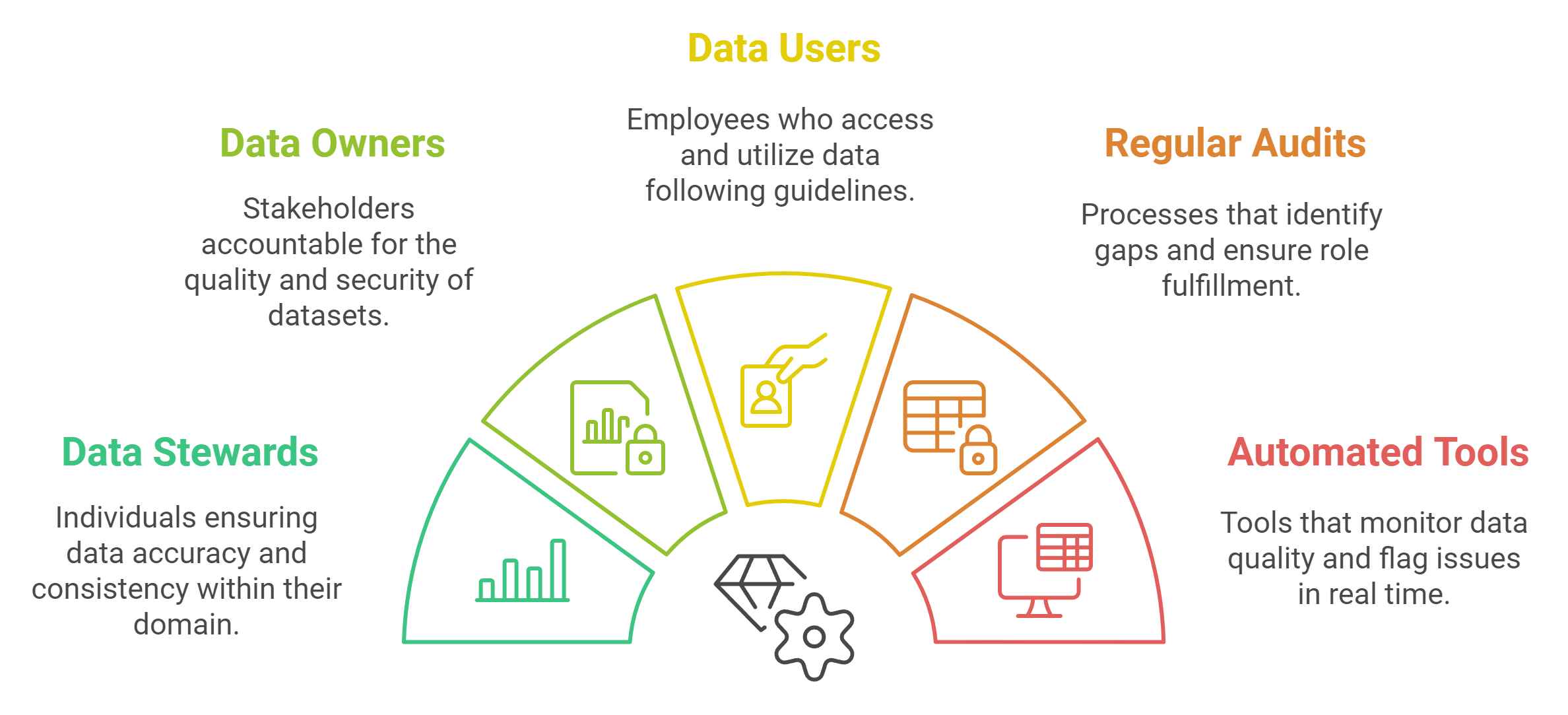
To address this issue, organizations must establish robust governance frameworks that define roles and responsibilities. These frameworks should include:
Data Stewards: Individuals responsible for ensuring data accuracy and consistency within their domain.
Data Owners: Stakeholders accountable for the overall quality and security of specific datasets.
Data Users: Employees who access and utilize data while adhering to established guidelines.
By implementing these roles, organizations can create a structured approach to data management. For example, a retail company might assign a data steward to oversee customer information, ensuring that records remain accurate and up-to-date. This approach reduces errors and enhances the reliability of the data.
Regular audits and reviews further strengthen accountability. These processes help identify gaps in data management and ensure that assigned roles are being fulfilled. Organizations can also use automated tools to monitor data quality and flag issues in real time. These tools provide an additional layer of oversight, ensuring that data remains accurate and actionable.
"Clear ownership transforms data from a liability into a strategic asset." This statement underscores the value of assigning responsibility for data management.
Inadequate accountability often results in missed opportunities and increased risks. For instance, incomplete customer records can hinder marketing efforts, while inaccurate financial data can lead to regulatory penalties. By prioritizing ownership and accountability, organizations can mitigate these risks and unlock the full potential of their data assets.
The Role of Data Governance in Addressing Data Quality Challenges
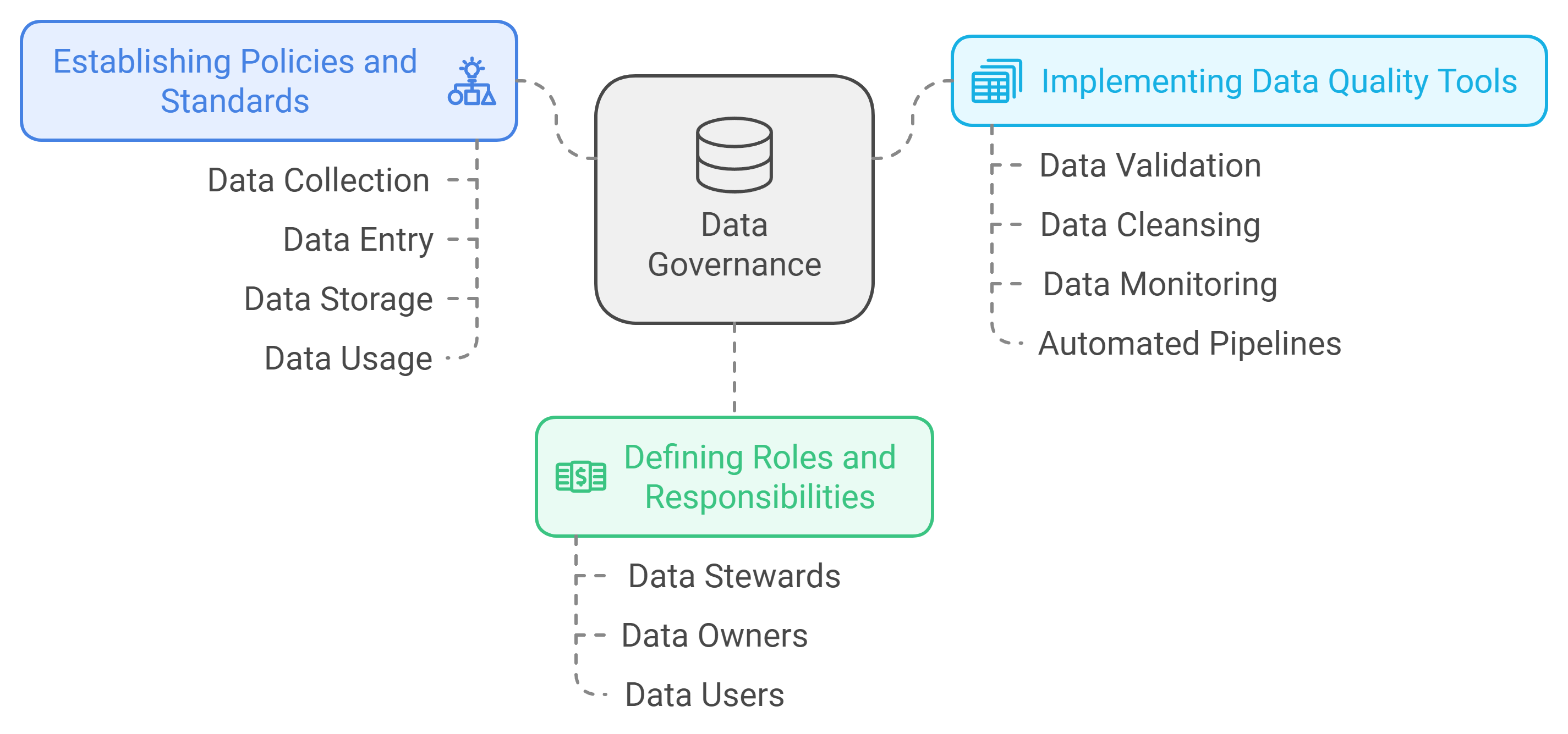
Establishing Policies and Standards for Data Management
Organizations often face data quality issues due to the absence of clear policies and standards. Without defined procedures, inconsistencies and errors become inevitable. Data governance plays a crucial role in addressing this challenge by establishing comprehensive guidelines for data collection, entry, storage, and usage. These policies ensure that data remains consistent and reliable across all systems.
For example, a retail company might struggle with pricing discrepancies due to varied data entry practices across branches. By implementing standardized protocols through data governance, the organization can enforce uniformity in how prices are recorded and updated. This approach minimizes errors and enhances trust in the data.
"Clear policies transform chaotic data into a structured and valuable resource." This principle underscores the importance of governance in creating a foundation for high-quality data.
Data governance frameworks also address inefficiencies in data architecture. They provide a structured approach to managing data repositories, ensuring that information is stored correctly and not duplicated across multiple locations. This reduces fragmentation and improves accessibility, enabling organizations to make better data-driven decisions.
Defining Roles and Responsibilities for Data Ownership
A lack of ownership and accountability often leads to fragmented data management. When no one takes responsibility for maintaining data quality, errors and inconsistencies proliferate. Data governance resolves this issue by defining clear roles and responsibilities for data ownership.
Organizations can assign specific roles such as data stewards, data owners, and data users. Data stewards oversee the accuracy and consistency of data within their domain. Data owners take accountability for the overall quality and security of specific datasets. Data users access and utilize data while adhering to established guidelines. This structured approach ensures that every aspect of data management has a designated point of accountability.
For instance, a healthcare organization might assign a data steward to manage patient records. This individual ensures that all information is accurate, complete, and up-to-date. Regular audits and reviews further strengthen accountability, identifying gaps and ensuring compliance with governance policies.
"Accountability is the cornerstone of effective data management." Assigning clear roles transforms data from a liability into a strategic asset.
By fostering a culture of accountability, organizations can mitigate risks associated with poor data quality. This approach builds trust among stakeholders and enhances the overall reliability of data.
Implementing Data Quality Tools and Technologies
Modern organizations generate vast amounts of data, making manual management impractical. Data governance frameworks address this challenge by integrating advanced tools and technologies designed to maintain data quality. These tools automate processes such as data validation, cleansing, and monitoring, reducing the likelihood of human error.
For example, automated data pipelines can ensure real-time updates, providing organizations with timely and accurate information. Financial institutions, for instance, rely on such tools to monitor market trends and make informed investment decisions. Delayed or inaccurate data could result in significant financial losses.
"Technology amplifies the effectiveness of governance by automating complex processes." This statement highlights the synergy between governance and technology in maintaining data quality.
Data quality tools also help organizations identify and resolve issues like missing or inconsistent data. They provide actionable insights, enabling businesses to address gaps proactively. By leveraging these technologies, organizations can enhance operational efficiency and unlock the full potential of their data assets.
Ensuring Compliance and Security Through Governance
Data governance plays a critical role in ensuring compliance and safeguarding data security. Organizations face increasing regulatory requirements and risks associated with data breaches. A robust governance framework provides the structure needed to address these challenges effectively.
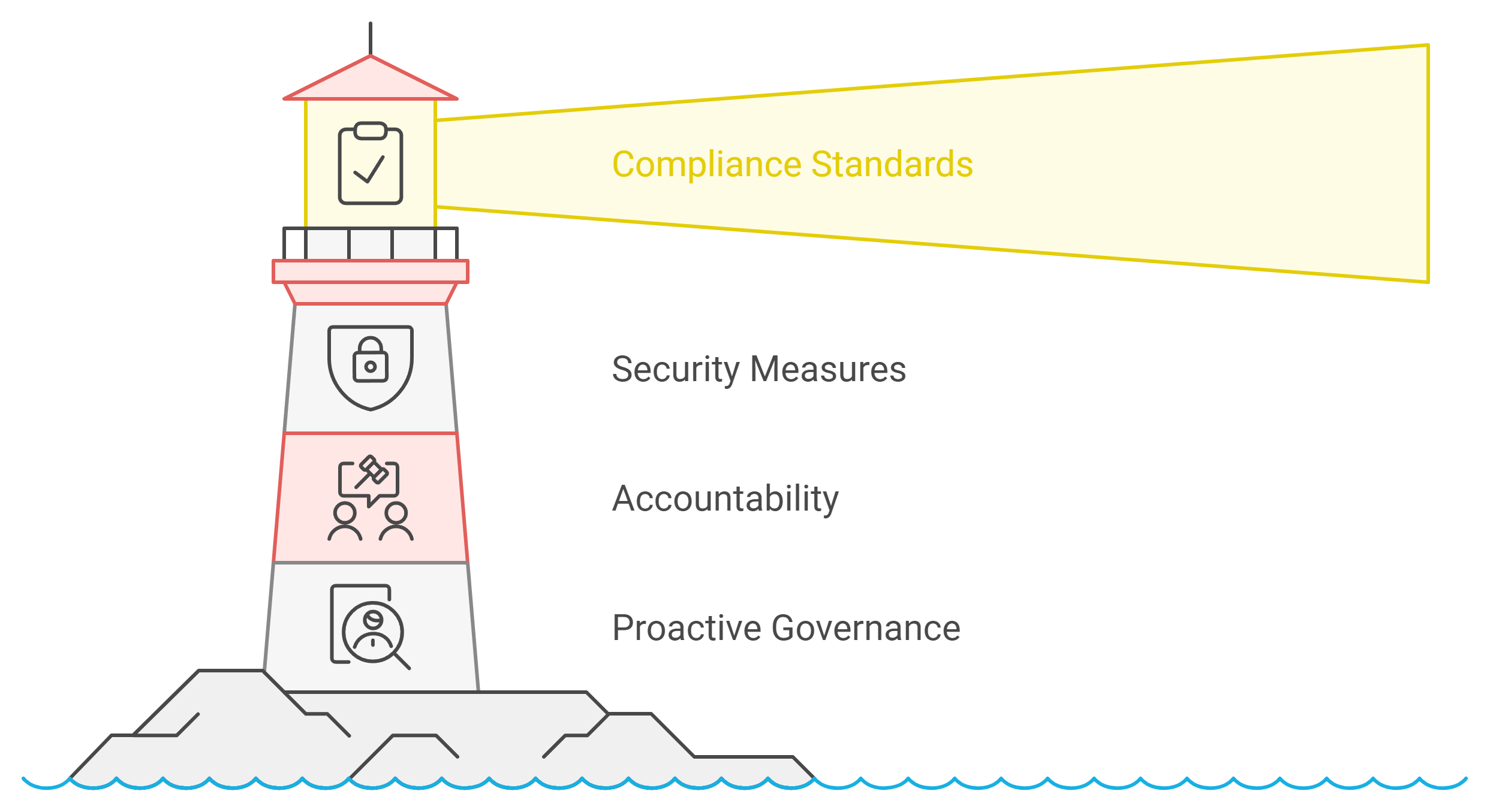
1. Establishing Clear Compliance Standards
Organizations must adhere to various legal and regulatory standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA. Data governance frameworks define clear policies and procedures to ensure compliance with these regulations. These policies guide how data is collected, stored, and processed, reducing the risk of violations.
For example, a healthcare organization managing patient records must comply with HIPAA regulations. Governance frameworks enforce strict access controls and audit trails to protect sensitive information. This approach minimizes the risk of non-compliance and associated penalties.
"Compliance is not optional; it is a necessity for building trust and avoiding legal repercussions."
By implementing governance policies, organizations can align their data practices with regulatory requirements. This alignment fosters transparency and accountability, enhancing stakeholder confidence.
2. Strengthening Data Security Measures
Data breaches pose significant risks to organizations, including financial losses and reputational damage. Governance frameworks establish robust security protocols to protect data from unauthorized access or misuse. These protocols include encryption, access controls, and regular security audits.
For instance, a retail company storing customer payment information must implement encryption to safeguard sensitive data. Governance frameworks ensure that only authorized personnel can access this information, reducing the likelihood of breaches.
"Strong governance transforms data security from a vulnerability into a strength."
Regular monitoring and incident response plans further enhance security. These measures enable organizations to detect and address threats promptly, minimizing potential damage.
3. Assigning Accountability for Compliance and Security
A lack of accountability often leads to gaps in compliance and security. Data governance frameworks assign specific roles and responsibilities to ensure that individuals take ownership of these critical areas. Data stewards oversee compliance with policies, while data owners ensure the security of their datasets.
For example, a financial institution might designate a data steward to monitor adherence to anti-money laundering regulations. This individual ensures that all transactions meet compliance standards, reducing the risk of violations.
"Accountability ensures that compliance and security are not just policies but practices embedded in daily operations."
By defining clear roles, organizations create a culture of responsibility. This culture strengthens their ability to maintain compliance and protect data assets.
4. Mitigating Risks Through Proactive Governance
Proactive governance helps organizations identify and address risks before they escalate. Regular audits and risk assessments provide insights into potential vulnerabilities. Governance frameworks use these insights to implement preventive measures, enhancing overall resilience.
For instance, an organization might conduct a security audit to identify outdated software that poses a risk. Governance policies mandate timely updates, reducing the likelihood of exploitation.
"Proactive governance turns potential risks into opportunities for improvement."
By prioritizing compliance and security, organizations can build a strong foundation for sustainable growth. Governance frameworks not only protect data but also enhance its value as a strategic asset.
Characteristics of Effective Data Governance Frameworks
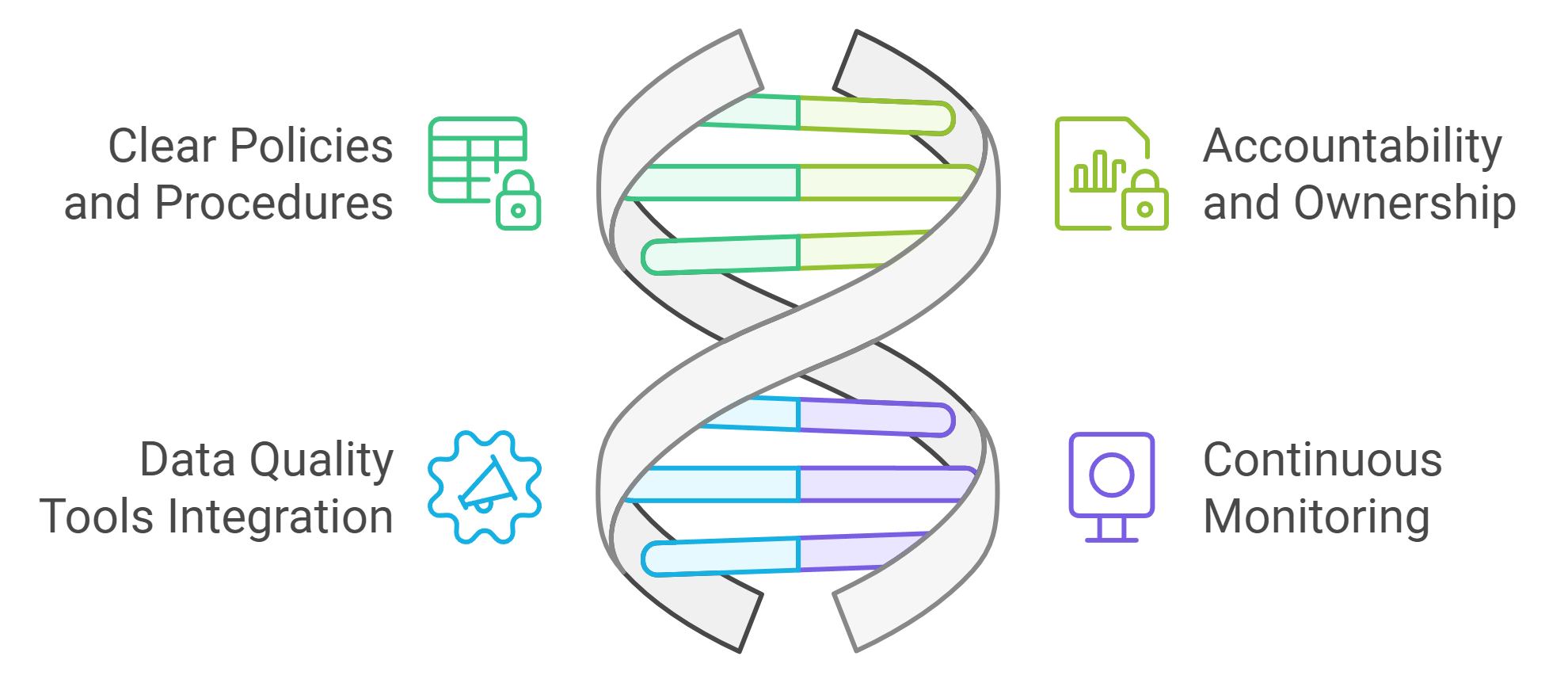
Clear Policies and Procedures
Effective data governance frameworks rely on well-defined policies and procedures. These guidelines establish the foundation for managing data consistently and accurately. Organizations use these policies to outline how data should be collected, stored, and processed. Clear instructions reduce ambiguity and ensure that all stakeholders follow the same standards.
For instance, a company might implement a policy requiring all customer data to be validated before entry into the system. This reduces errors and ensures data accuracy. Procedures also help organizations address data inconsistencies by providing step-by-step instructions for resolving issues. Regular updates to these policies ensure they remain relevant as organizational needs evolve.
"Clear policies transform chaotic data into a structured and valuable resource." This principle highlights the importance of governance in creating a reliable data management system.
Organizations with strong governance frameworks also conduct regular training sessions. These sessions educate employees about the policies and their roles in maintaining data quality. By fostering a culture of adherence to these guidelines, organizations can enhance the reliability and integrity of their data.
Accountability and Ownership Structures
Accountability and ownership structures form the backbone of effective data governance. Assigning clear roles ensures that individuals or teams take responsibility for managing data quality and addressing inconsistencies. Without accountability, errors often go unnoticed, leading to unreliable data.
Data stewards play a critical role in this structure. They oversee the accuracy and consistency of data within their domains. Data owners, on the other hand, hold ultimate responsibility for the quality and security of specific datasets. These roles create a structured approach to data management, ensuring that every aspect has a designated point of accountability.
"Accountability is the cornerstone of effective data management." This statement emphasizes the importance of assigning responsibility to maintain high-quality data.
For example, a healthcare organization might assign a data steward to manage patient records. This individual ensures that all information remains accurate and up-to-date. Regular audits further strengthen accountability by identifying gaps and ensuring compliance with governance policies. By fostering a culture of responsibility, organizations can mitigate risks and build trust in their data.
Integration of Data Quality Tools
Modern organizations generate vast amounts of data, making manual management impractical. Effective data governance frameworks integrate advanced tools and technologies to maintain data quality. These tools automate processes like data validation, cleansing, and monitoring, reducing the likelihood of human error.
For example, automated data pipelines ensure real-time updates, providing organizations with timely and accurate information. Financial institutions often rely on such tools to monitor market trends and make informed decisions. Delayed or inaccurate data could result in significant financial losses.
"Technology amplifies the effectiveness of governance by automating complex processes." This statement highlights the synergy between governance and technology in maintaining data quality.
Data quality tools also help organizations identify and resolve issues like missing or inconsistent data. They provide actionable insights, enabling businesses to address gaps proactively. By leveraging these technologies, organizations can enhance operational efficiency and unlock the full potential of their data assets.
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Continuous monitoring and improvement form the backbone of effective data governance. Organizations must actively oversee their data processes to ensure ongoing accuracy, consistency, and reliability. This proactive approach helps identify issues early, enabling timely corrections and fostering a culture of accountability.
1. The Importance of Regular Audits
Regular audits play a critical role in maintaining data quality. These audits evaluate data for errors, inconsistencies, or gaps, ensuring that it meets organizational standards. By conducting routine checks, organizations can uncover hidden issues that might compromise decision-making or operational efficiency.
For example, a financial institution might perform monthly audits to verify the accuracy of transaction records. This practice reduces the risk of errors that could lead to regulatory penalties or customer dissatisfaction. Audits also provide valuable insights into areas requiring improvement, helping organizations refine their data management practices.
"Managing data quality is considered by many researchers to be an important reason for adopting data governance." This statement underscores the necessity of regular evaluations to uphold data integrity.
2. Leveraging Automation for Real-Time Monitoring
Automation enhances the effectiveness of continuous monitoring. Advanced tools and technologies can track data quality in real time, flagging anomalies or inconsistencies as they occur. These tools reduce reliance on manual processes, minimizing human error and improving efficiency.
For instance, automated data pipelines can monitor the timeliness and accuracy of incoming data. A retail company might use such tools to ensure that inventory levels remain up-to-date across all locations. This real-time oversight prevents stock discrepancies and supports better decision-making.
"Technology amplifies the effectiveness of governance by automating complex processes." Automation not only streamlines monitoring but also ensures that data remains actionable and reliable.
3. Encouraging Accountability Through Data Stewardship
Accountability is essential for continuous improvement. Data stewards, as key players in governance frameworks, oversee the quality and consistency of data within their domains. They take responsibility for addressing issues and implementing corrective measures.
Organizations can assign data stewards to specific datasets or departments. For example, a healthcare provider might designate a steward to manage patient records, ensuring that all information remains accurate and complete. This role fosters a sense of ownership, motivating individuals to maintain high standards.
"Data governance often means giving accountability and responsibility for both the data itself and the processes that ensure its proper use to 'data stewards.'" Assigning clear roles strengthens the overall governance framework.
4. Adopting a Culture of Continuous Improvement
A culture of continuous improvement encourages organizations to view data governance as an evolving process. Regular training sessions, feedback loops, and performance reviews help employees stay aligned with governance objectives. These initiatives promote a mindset of learning and adaptation, ensuring that governance practices remain effective over time.
For instance, a company might hold quarterly workshops to educate employees on new data management tools or policies. These sessions empower staff to contribute to governance efforts, enhancing the overall quality of data.
"Data governance roles and responsibilities involve measures to ensure that data is accurate and reliable and determine steps to be taken to manage and maintain data integrity." This principle highlights the importance of ongoing efforts to refine governance practices.
5. Measuring Success Through Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Organizations should establish KPIs to measure the success of their monitoring and improvement efforts. Metrics such as error rates, data completeness, and processing times provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of governance frameworks. Regularly reviewing these indicators helps organizations identify trends and make informed adjustments.
For example, a logistics company might track the accuracy of delivery data as a KPI. A decline in accuracy could signal the need for additional training or system upgrades. By monitoring these metrics, organizations can ensure that their governance efforts yield tangible results.
"Clear ownership transforms data from a liability into a strategic asset." Measuring progress reinforces the value of governance in achieving organizational goals.
Continuous monitoring and improvement ensure that data governance remains a dynamic and effective process. By combining regular audits, automation, accountability, and a commitment to learning, organizations can maintain high-quality data that drives success.
Real-World Examples of Data Governance Enhancing Data Quality
Case Study: Financial Sector Governance Frameworks
The financial sector demonstrates the transformative power of data governance in ensuring data quality. Financial institutions rely heavily on accurate and consistent data for decision-making, regulatory compliance, and risk management. A robust governance framework enables these organizations to manage vast amounts of sensitive data effectively.
For instance, many banks have implemented centralized data governance frameworks to address data silos and inconsistencies. These frameworks establish clear policies for data collection, storage, and usage. By standardizing data formats and definitions, banks ensure consistency across systems. This approach reduces errors in financial reporting and enhances trust among stakeholders.
"Data governance frameworks enhance data quality, accuracy, and value within organizations." This principle is evident in the financial sector, where governance ensures data integrity and reliability.
Additionally, financial institutions use advanced data quality tools supported by governance frameworks. These tools automate processes like data validation and cleansing, minimizing human error. For example, automated systems flag discrepancies in transaction records, enabling quick resolution. This proactive approach improves operational efficiency and supports better decision-making.
Case Study: Healthcare Data Quality Improvements
The healthcare industry provides another compelling example of data governance enhancing data quality. Accurate and reliable data is critical for patient care, research, and compliance with regulations like HIPAA. Governance frameworks play a pivotal role in managing this data effectively.
Hospitals and healthcare providers often face challenges like fragmented patient records and inconsistent data entry practices. Data governance addresses these issues by establishing unified standards and protocols. For example, a hospital might implement a governance framework that enforces standardized formats for patient information. This ensures consistency across departments and reduces errors in diagnosis or treatment.
"Improving data quality within a data governance program ensures data accuracy, completeness, relevance, and credibility." This statement highlights the importance of governance in healthcare settings.
Healthcare organizations also leverage data governance to enhance compliance and security. Governance frameworks define access controls and audit trails, protecting sensitive patient information. Regular audits ensure adherence to these policies, minimizing risks associated with data breaches. By prioritizing governance, healthcare providers improve data quality and build trust with patients and regulators.
Lessons Learned from Successful Implementations
Real-world examples reveal valuable lessons about the role of data governance in enhancing data quality. These lessons highlight the importance of strategic planning, accountability, and continuous improvement.
Establish Clear Policies and Standards
Organizations must define comprehensive guidelines for data management. Clear policies reduce ambiguity and ensure consistency across systems. For example, financial institutions benefit from standardized data formats that enhance accuracy and reliability.Leverage Advanced Tools and Technologies
Data quality tools become more effective when integrated into governance frameworks. Automation reduces manual errors and improves efficiency. Healthcare providers, for instance, use automated systems to maintain accurate patient records.Foster Accountability and Ownership
Assigning specific roles ensures accountability for data quality. Data stewards and owners play critical roles in maintaining accuracy and consistency. This structured approach minimizes errors and enhances trust in the data.Prioritize Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Regular audits and real-time monitoring help organizations identify and address issues promptly. Proactive governance ensures that data remains accurate, complete, and relevant over time.
"Good data governance practices lead to more reliable decision-making by ensuring accurate, consistent, and trustworthy data." This insight underscores the long-term benefits of investing in governance frameworks.
By learning from these examples, organizations can implement effective data governance strategies. These strategies not only enhance data quality but also unlock the full potential of data as a strategic asset.
Strategies for Sustaining Data Quality Through Governance
Continuous Monitoring and Auditing Processes
Continuous monitoring and auditing processes ensure that data quality remains consistent over time. Organizations must actively evaluate their data to identify errors, inconsistencies, or gaps. Regular audits provide a structured approach to assessing data accuracy and reliability. These evaluations help organizations detect issues early, reducing the risk of flawed decision-making.
For example, financial institutions often conduct monthly audits to verify transaction records. This practice ensures compliance with regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI-DSS). By adhering to these standards, organizations safeguard sensitive information and maintain trust among stakeholders.
Automated tools enhance the effectiveness of monitoring processes. These tools track data in real time, flagging anomalies as they occur. For instance, a logistics company might use automated systems to monitor inventory levels across multiple warehouses. This approach minimizes human error and ensures timely updates, supporting operational efficiency.
"Regular audits and real-time monitoring form the backbone of effective data governance." This principle highlights the importance of proactive oversight in maintaining high-quality data.
Organizations should also establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of their monitoring efforts. Metrics such as error rates and data completeness provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of governance frameworks. By reviewing these indicators regularly, businesses can refine their strategies and ensure continuous improvement.
Adapting Governance Frameworks to Changing Needs
The dynamic nature of business environments requires organizations to adapt their governance frameworks to evolving needs. Static frameworks often fail to address emerging challenges, such as new regulatory requirements or technological advancements. Flexibility ensures that governance practices remain relevant and effective.
For instance, the introduction of laws like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) has increased the need for robust data privacy measures. Organizations must update their governance policies to comply with these regulations, reducing the risk of penalties and reputational damage.
Technological advancements also necessitate changes in governance frameworks. The rise of artificial intelligence and machine learning has transformed data management practices. Organizations must integrate these technologies into their frameworks to enhance data quality and operational efficiency. For example, automated data cleansing tools can streamline processes and reduce errors.
"Adaptability is the key to sustaining data quality in a rapidly changing world." This statement underscores the importance of evolving governance practices to meet new challenges.
Regular reviews of governance frameworks help organizations identify areas for improvement. These reviews should involve input from all stakeholders, ensuring that policies align with organizational goals and industry standards. By fostering a culture of adaptability, businesses can maintain high-quality data and stay ahead of the competition.
Building a Culture of Data Stewardship
A strong culture of data stewardship ensures that all employees take responsibility for maintaining data quality. Data stewards play a critical role in overseeing the accuracy and consistency of information within their domains. However, fostering a culture of stewardship requires more than assigning roles—it involves educating employees and promoting accountability.
Training programs help employees understand the importance of data quality and their role in governance efforts. For example, a healthcare organization might conduct workshops on managing patient records in compliance with HIPAA. These sessions empower staff to contribute to governance objectives, enhancing the overall reliability of data.
"Data stewardship transforms individuals into guardians of organizational data." This principle highlights the value of promoting accountability at all levels.
Organizations should also recognize and reward employees who demonstrate excellence in data management. Incentives encourage staff to prioritize data quality, fostering a sense of ownership. For instance, a retail company might reward team members who identify and resolve data discrepancies, reinforcing the importance of stewardship.
Collaboration further strengthens a culture of stewardship. Cross-departmental teams can work together to address data quality challenges, sharing insights and best practices. This collaborative approach ensures that governance efforts remain cohesive and effective.
By building a culture of data stewardship, organizations create a foundation for sustained data quality. Employees become active participants in governance efforts, ensuring that data remains accurate, consistent, and reliable.
Leveraging Emerging Technologies for Data Management
Emerging technologies have revolutionized data management by introducing innovative tools and methods that enhance efficiency, accuracy, and security. Organizations now rely on these advancements to address complex data challenges and maintain high-quality standards. By integrating cutting-edge solutions, businesses can streamline processes, reduce errors, and unlock the full potential of their data assets.
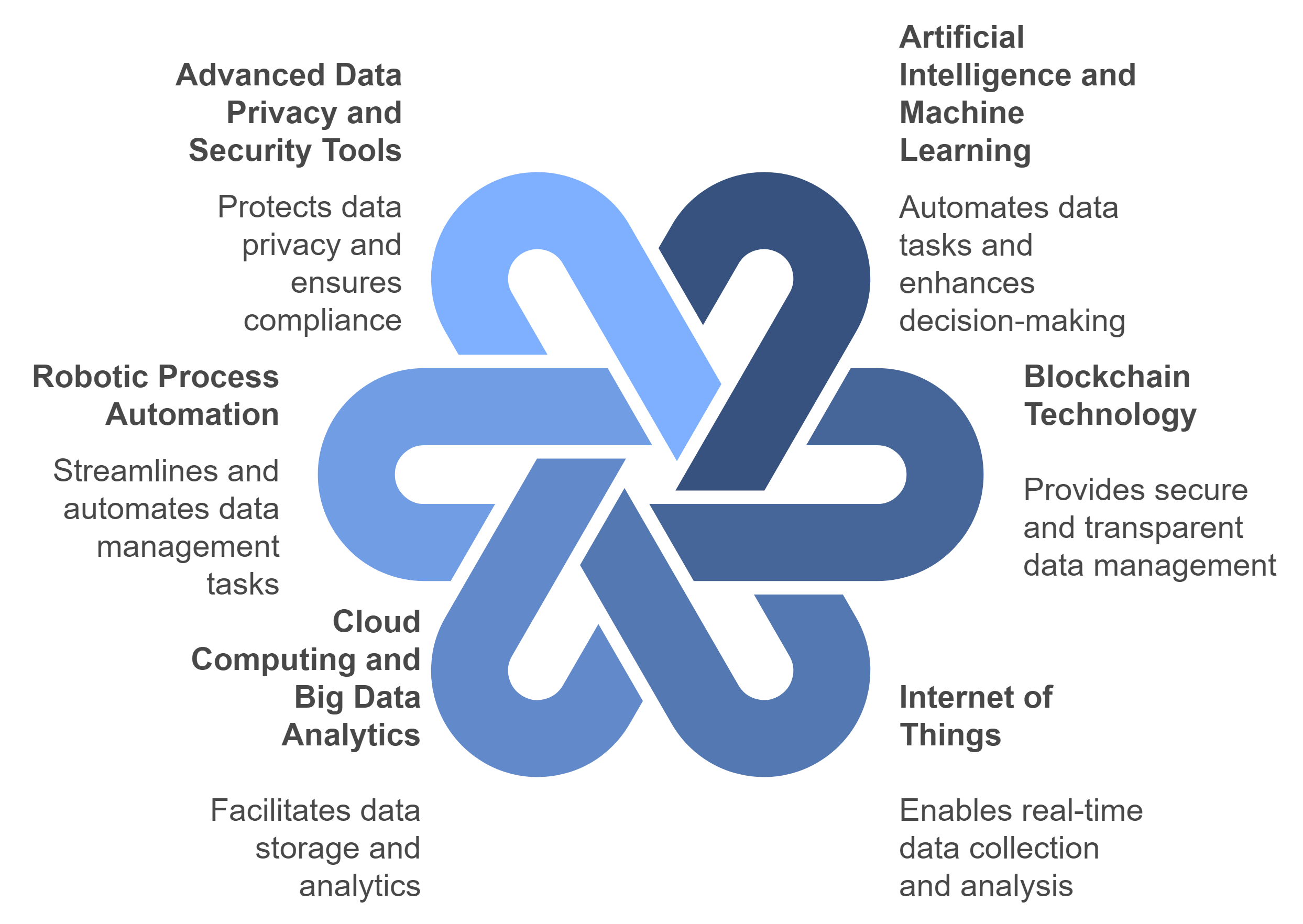
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML have transformed how organizations manage and analyze data. These technologies automate repetitive tasks, such as data cleansing and validation, ensuring greater accuracy and consistency. AI-powered algorithms can detect anomalies, identify patterns, and predict trends, enabling proactive decision-making.
For instance, financial institutions use AI to monitor transactions for fraudulent activities. Machine learning models analyze vast datasets in real time, flagging suspicious behavior and reducing risks. This approach not only enhances data quality but also strengthens compliance with regulations like the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI-DSS).
"AI and ML empower organizations to turn raw data into actionable insights, driving smarter decisions and improved outcomes."
2. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent method for managing data. Its decentralized nature ensures that data remains tamper-proof and traceable, making it ideal for industries requiring high levels of trust and accountability. Blockchain creates an immutable record of transactions, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
Healthcare providers, for example, leverage blockchain to manage patient records securely. This technology ensures compliance with privacy laws such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) by safeguarding sensitive information. Blockchain also facilitates data sharing among stakeholders while maintaining confidentiality and integrity.
"Blockchain redefines data security by providing a transparent and tamper-resistant framework for managing sensitive information."
3. Internet of Things (IoT)
The IoT generates massive amounts of data from interconnected devices, creating new opportunities for data-driven insights. However, managing this influx of information requires robust governance frameworks and advanced technologies. IoT platforms enable organizations to collect, process, and analyze data in real time, ensuring timeliness and relevance.
Logistics companies, for instance, use IoT sensors to track shipments and monitor inventory levels. These devices provide real-time updates, allowing businesses to optimize operations and respond to disruptions effectively. By integrating IoT with data governance practices, organizations can ensure that the data collected remains accurate and actionable.
"IoT bridges the gap between physical and digital worlds, delivering real-time insights that drive operational efficiency."
4. Cloud Computing and Big Data Analytics
Cloud computing has revolutionized data storage and accessibility. It allows organizations to store vast amounts of data securely while providing on-demand access to authorized users. Cloud platforms also support big data analytics, enabling businesses to process and analyze large datasets efficiently.
Retail companies often use cloud-based analytics tools to understand customer behavior and preferences. These insights help tailor marketing strategies and improve customer experiences. Additionally, cloud solutions ensure compliance with regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) by offering robust security measures and data privacy controls.
"Cloud computing and big data analytics empower organizations to harness the power of their data, driving innovation and growth."
5. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA automates routine data management tasks, reducing human error and improving efficiency. These tools handle processes such as data entry, extraction, and migration, freeing up employees to focus on strategic initiatives. RPA also ensures consistency by following predefined rules and protocols.
For example, banks use RPA to streamline customer onboarding processes. Automated systems verify documents, update records, and ensure compliance with regulations like the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA). This approach enhances data quality while minimizing operational costs.
"RPA transforms repetitive tasks into seamless workflows, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in data management."
6. Advanced Data Privacy and Security Tools
Emerging technologies have introduced sophisticated tools for safeguarding data privacy and security. Encryption, multi-factor authentication, and intrusion detection systems protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. These tools help organizations comply with laws like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the GDPR, reducing the risk of penalties and reputational damage.
For instance, e-commerce platforms use advanced security measures to protect customer payment information. These technologies ensure that data remains confidential and secure, fostering trust among users.
"Advanced security tools fortify data defenses, ensuring compliance and instilling confidence in stakeholders."
By leveraging emerging technologies, organizations can enhance their data management capabilities and maintain high-quality standards. These innovations not only address current challenges but also prepare businesses for future demands, ensuring long-term success in an increasingly data-driven world.
The Long-Term Benefits of Data Governance for Organizations
Improved Decision-Making Through Reliable Data
Reliable data serves as the cornerstone of effective decision-making. Data governance ensures that organizations maintain accurate, consistent, and trustworthy data. By implementing clear policies and procedures, businesses can eliminate discrepancies and errors in their datasets. This consistency allows decision-makers to rely on the information without second-guessing its validity.
For example, a retail company analyzing customer purchasing trends can make informed decisions about inventory management when the data is accurate and up-to-date. Without governance, errors such as duplicate entries or missing records could lead to flawed conclusions. By prioritizing data governance, organizations create a foundation for strategic planning and operational success.
"Accurate data leads to better decisions, while unreliable data creates uncertainty and risk." This principle highlights the importance of governance in fostering confidence in organizational insights.
Organizations also benefit from enhanced transparency through governance frameworks. Clear documentation of data sources and processes enables stakeholders to trace the origins of information. This traceability builds trust and ensures that decisions are based on credible evidence.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency and Risk Mitigation
Operational efficiency improves significantly when data governance frameworks are in place. Standardized processes for data collection, storage, and usage reduce redundancies and streamline workflows. Employees spend less time resolving data-related issues and more time focusing on core tasks.
For instance, a logistics company managing supply chain data can optimize routes and reduce delivery times when the information is consistent and accessible. Governance frameworks eliminate inefficiencies caused by fragmented or siloed data, enabling seamless integration across departments.
"Efficiency thrives when data flows smoothly through well-defined governance structures." This statement underscores the role of governance in enhancing productivity.
Risk mitigation is another critical benefit of data governance. Poor data quality often leads to financial losses, reputational damage, and missed opportunities. Governance frameworks address these risks by enforcing strict standards for data accuracy and security. Regular audits and monitoring processes help identify potential vulnerabilities before they escalate.
For example, financial institutions use governance to comply with anti-money laundering regulations. By maintaining accurate transaction records and monitoring for anomalies, these organizations reduce the risk of regulatory penalties and fraud.
Strengthened Compliance and Security Measures
Compliance with legal and regulatory standards becomes more manageable with robust data governance. Organizations face increasing scrutiny from laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). Governance frameworks define the policies and procedures necessary to meet these requirements, reducing the risk of non-compliance.
For example, a healthcare provider must adhere to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) when managing patient records. Data governance ensures that access controls, encryption, and audit trails are in place to protect sensitive information. These measures safeguard privacy and build trust among patients and regulators.
"Compliance is not just a legal obligation; it is a foundation for building trust and credibility." This insight emphasizes the value of governance in fostering transparency and accountability.
Security measures also improve under governance frameworks. Organizations can implement robust protocols to protect data from breaches and unauthorized access. Encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits become integral components of governance strategies. These efforts not only protect sensitive information but also enhance the organization's reputation as a trusted entity.
By prioritizing compliance and security, organizations reduce the likelihood of costly penalties and reputational damage. Governance transforms data from a potential liability into a valuable asset that drives growth and innovation.
Data governance serves as the cornerstone for achieving and sustaining data quality. It establishes structured frameworks that ensure data remains accurate, consistent, and reliable. Maintaining data quality requires ongoing effort, as 42% of data leaders fail to monitor or measure their governance practices. Organizations must prioritize governance to optimize data for business processes, a goal shared by 61% of companies. By embedding governance into their operations, businesses unlock the full potential of their data assets, driving productivity and informed decision-making.
See Also
Unveiling Data Governance Essentials with George Firican
Merging Data Leadership Within Corporate Governance Frameworks
Data Leadership's Impact on Digital Transformation Success
Addressing Obstacles in Effective Data Leadership
Exploring Data Governance and Agile Synergy with Gustavo Morcuende
