The EU AI Act and the Future of Autonomous Systems
The EU AI Act represents a groundbreaking step in regulating artificial intelligence. By focusing on risk assessment and data governance, it ensures that autonomous systems operate safely and ethically. This legislation, in effect since August 1, 2023, sets a global benchmark for responsible AI development. You will see how it balances innovation with safety, fostering trust in AI technologies. Its emphasis on protecting fundamental rights and promoting transparency makes it a vital framework for shaping the future of autonomous systems.
Key Takeaways
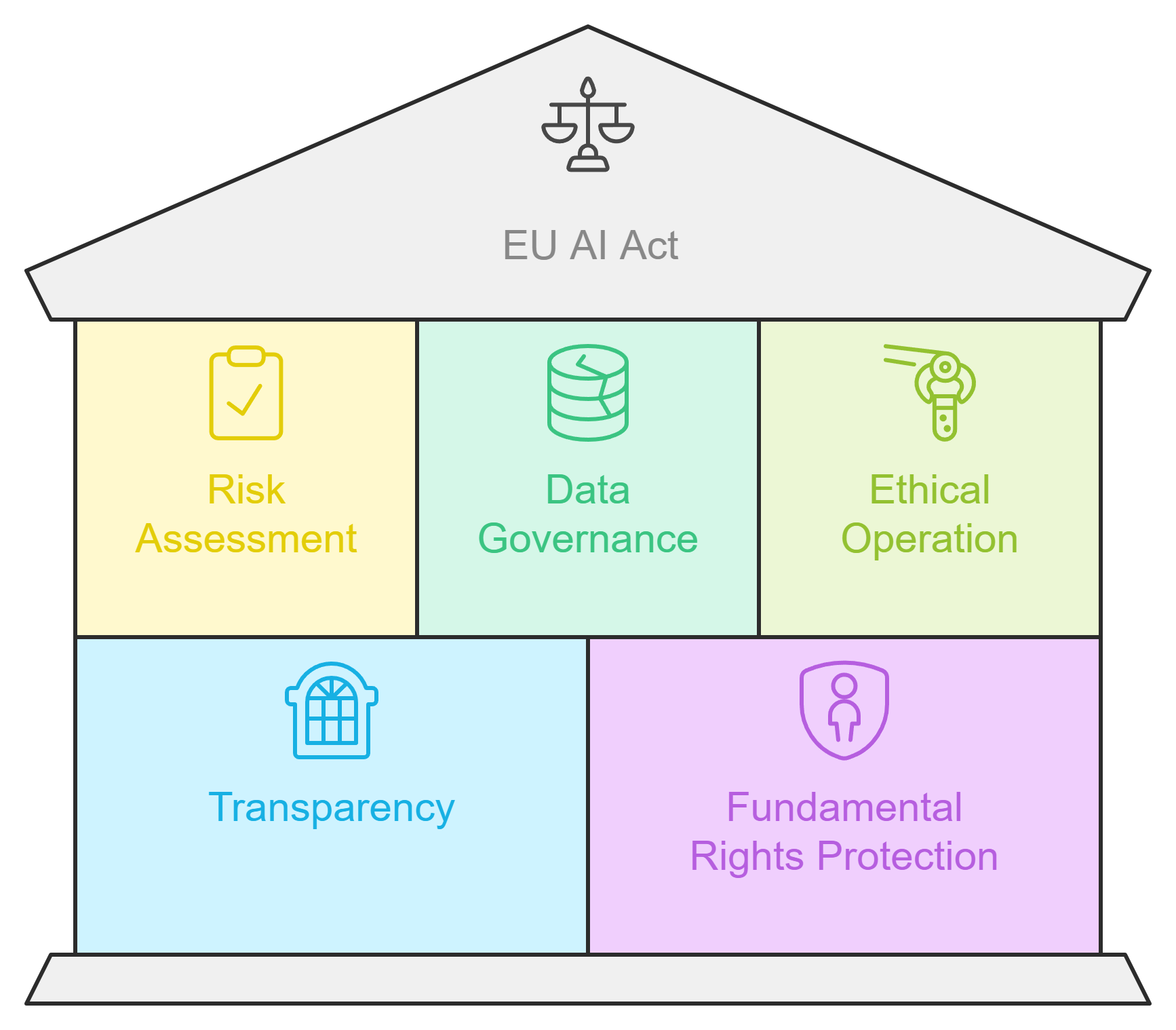
The EU AI Act establishes a risk-based governance framework, categorizing AI systems into four risk levels to ensure appropriate regulation and safety.
Compliance with the Act is crucial for developers of high-risk AI systems, requiring thorough risk assessments and adherence to strict safety and transparency standards.
Transparency and explainability are essential; developers must provide clear documentation about their systems' functions and limitations to build user trust.
Human oversight mechanisms are necessary to allow for intervention in autonomous systems, ensuring ethical use and reducing the risk of harm.
The Act positions the EU as a global leader in AI regulation, encouraging other regions to adopt similar ethical standards and fostering international collaboration.
Investing in training and compliance measures is vital for organizations to navigate the regulatory landscape while promoting innovation in AI technologies.
The EU AI Act's emphasis on ethical innovation encourages developers to create responsible AI solutions that respect fundamental rights and societal values.
Overview of the EU AI Act
The EU AI Act stands as a pioneering framework designed to regulate artificial intelligence systems. It addresses the challenges posed by AI while fostering innovation and ensuring safety. By establishing clear guidelines, the Act aims to create a balanced environment where technology can thrive without compromising fundamental rights or societal values.
Purpose and scope of the EU AI Act
The EU AI Act serves multiple purposes. It ensures that AI systems operate in ways that respect human rights, promote safety, and uphold democratic principles. The Act applies to all AI systems used within the European Union, regardless of whether they were developed locally or imported. This broad scope ensures consistent standards across all Member States, creating a unified approach to AI governance.
The Act also categorizes AI systems based on their potential risks. This classification allows regulators to focus on high-risk systems, such as those used in healthcare, transportation, and law enforcement. By doing so, the Act protects citizens from harmful AI applications while encouraging the development of trustworthy and human-centric technologies.
Key principles of the EU AI Act
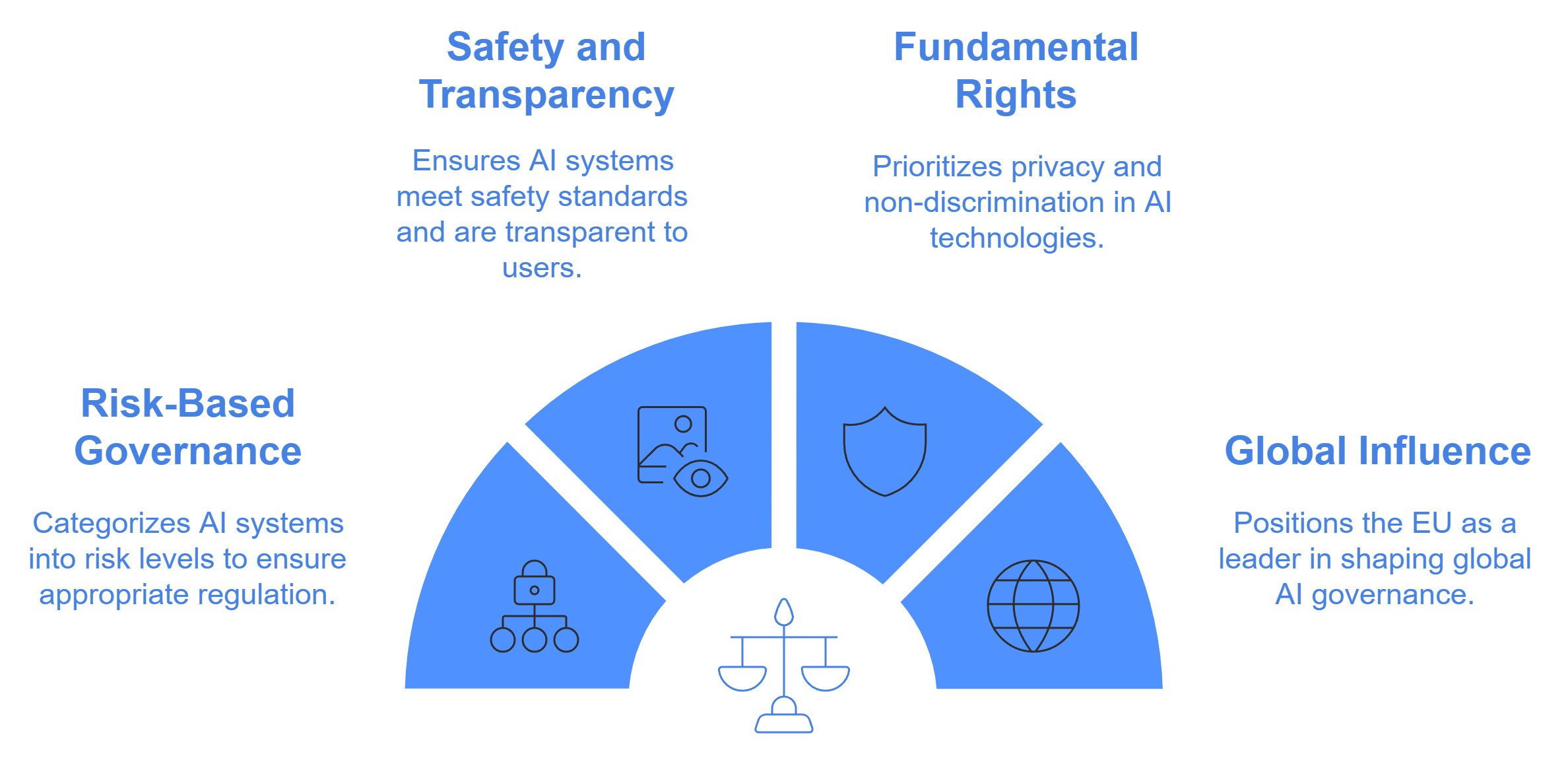
Risk-based governance framework
The EU AI Act introduces a risk-based governance framework to manage AI systems effectively. This framework categorizes AI into four risk levels: unacceptable, high, limited, and minimal. Systems deemed "unacceptable," such as those violating fundamental rights, face outright bans. High-risk systems must comply with strict requirements, including risk assessments and transparency measures. This approach ensures that the level of regulation matches the potential impact of the AI system.
Emphasis on safety, transparency, and fundamental rights
Safety and transparency lie at the heart of the EU AI Act. Developers must ensure that their AI systems meet rigorous safety standards to prevent harm. Transparency requirements mandate clear documentation and disclosures, enabling users to understand how these systems function. The Act also prioritizes fundamental rights, such as privacy and non-discrimination, ensuring that AI technologies align with ethical principles and societal values.
The EU AI Act's role in global AI regulation
The EU AI Act sets a global benchmark for AI governance. Its comprehensive framework influences not only European companies but also international organizations seeking to enter the EU market. By promoting ethical and human-centric AI, the Act encourages other regions to adopt similar standards. This leadership positions the European Union as a key player in shaping the future of AI regulation worldwide.
"The EU AI Act is not just a regional regulation; it is a global statement on how AI should serve humanity responsibly."
The Act's emphasis on trust and accountability inspires confidence in AI technologies, paving the way for international collaboration. As more countries align their regulations with the EU's standards, the world moves closer to a harmonized approach to AI governance.
Key Provisions of the EU AI Act for Autonomous Systems
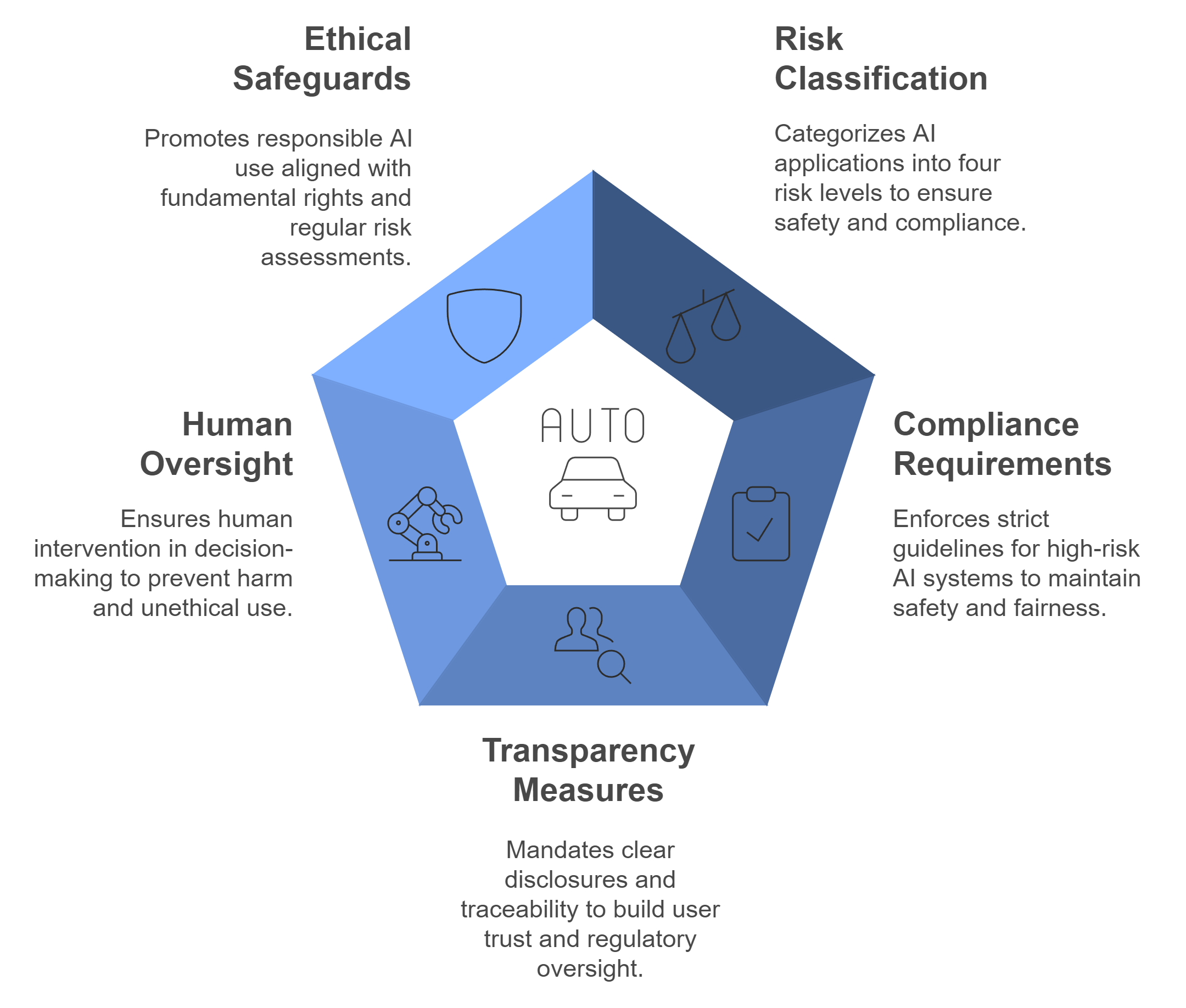
Risk classification and its impact on autonomous systems
The EU AI Act introduces a structured risk classification system that directly impacts how autonomous systems are regulated. This system categorizes AI applications into four levels: unacceptable, high, limited, and minimal risk. Autonomous systems often fall under the high-risk category due to their potential to affect safety, privacy, and fundamental rights.
High-risk AI systems and compliance requirements
If you develop or deploy high-risk AI systems, you must meet strict compliance requirements. These include conducting conformity assessments to ensure your system aligns with the Act's standards. Post-market surveillance becomes essential to monitor the system's performance and address any emerging risks. You also need to implement robust data governance practices to ensure data accuracy, security, and fairness. These measures aim to minimize harm while fostering trust in autonomous technologies.
Prohibited AI practices and their implications
The Act explicitly bans certain AI practices deemed to pose unacceptable risks. For example, systems that exploit vulnerabilities of specific groups or use subliminal techniques to manipulate behavior are prohibited. If you operate in the AI space, understanding these restrictions is crucial. Violating these rules can lead to severe penalties, including fines and market bans. By adhering to these guidelines, you contribute to creating ethical and responsible AI systems.
Transparency and accountability measures
Transparency and accountability form the backbone of the EU AI Act. These principles ensure that users and regulators can understand and trust autonomous systems. As a developer or operator, you must prioritize these aspects to comply with the Act and build user confidence.
Mandatory disclosures for autonomous systems
You must provide clear and accessible documentation for your autonomous systems. This includes details about the system's purpose, functionality, and limitations. Users should know how the system operates and what data it processes. These disclosures help users make informed decisions and reduce the risk of misuse. Transparency also facilitates regulatory oversight, ensuring your system meets the required standards.
Ensuring explainability and traceability
Explainability and traceability are critical for building trust in autonomous systems. You need to design your systems so users can understand their decision-making processes. Traceability involves maintaining detailed records of the system's development and operation. These records allow you to identify and address issues quickly. By focusing on these aspects, you enhance the reliability and accountability of your AI solutions.
Human oversight and ethical safeguards
Human oversight and ethical safeguards are essential for the responsible deployment of autonomous systems. The EU AI Act emphasizes the importance of these elements to prevent harm and ensure ethical use.
The role of human intervention in decision-making
You must incorporate mechanisms for human intervention in your autonomous systems. These mechanisms allow humans to override decisions or halt operations when necessary. This ensures that your systems do not operate unchecked, especially in high-stakes scenarios. Human oversight acts as a safety net, reducing the likelihood of errors or unethical outcomes.
Preventing harm and ensuring ethical use
Ethical safeguards are vital for preventing harm and promoting responsible AI use. You should design your systems to align with fundamental rights, such as privacy and non-discrimination. Regular risk assessments help you identify and mitigate potential harms. By prioritizing ethics, you not only comply with the Act but also contribute to the broader goal of trustworthy AI.
Compliance Requirements for Autonomous Systems Under the EU AI Act
Conducting risk assessments
Identifying and mitigating risks in autonomous systems
You must conduct thorough risk assessments to ensure your autonomous systems comply with the EU AI Act. Start by identifying potential risks that could arise from your system's operation. These risks may include safety concerns, privacy violations, or biases in decision-making. Once identified, take proactive steps to mitigate these risks. For example, you can implement robust testing protocols to evaluate system performance under various conditions. By addressing risks early, you enhance the reliability and safety of your technology.
The EU AI Act's risk-based approach ensures that high-risk systems, such as those used in healthcare or transportation, receive the most scrutiny. This focus on risk management not only protects users but also builds trust in your autonomous solutions.
Documentation and reporting obligations
The EU AI Act requires detailed documentation for all high-risk AI systems. You must maintain records that outline your system's design, development process, and intended purpose. These records should also include information about the data used to train your AI and the measures taken to ensure its accuracy and fairness.
Regular reporting is another critical obligation. You need to provide updates on your system's performance and any incidents that may occur. This transparency allows regulators to monitor compliance and ensures accountability. By keeping comprehensive documentation, you not only meet legal requirements but also create a valuable resource for troubleshooting and improving your system.
Ensuring transparency and user understanding
Designing systems for explainability
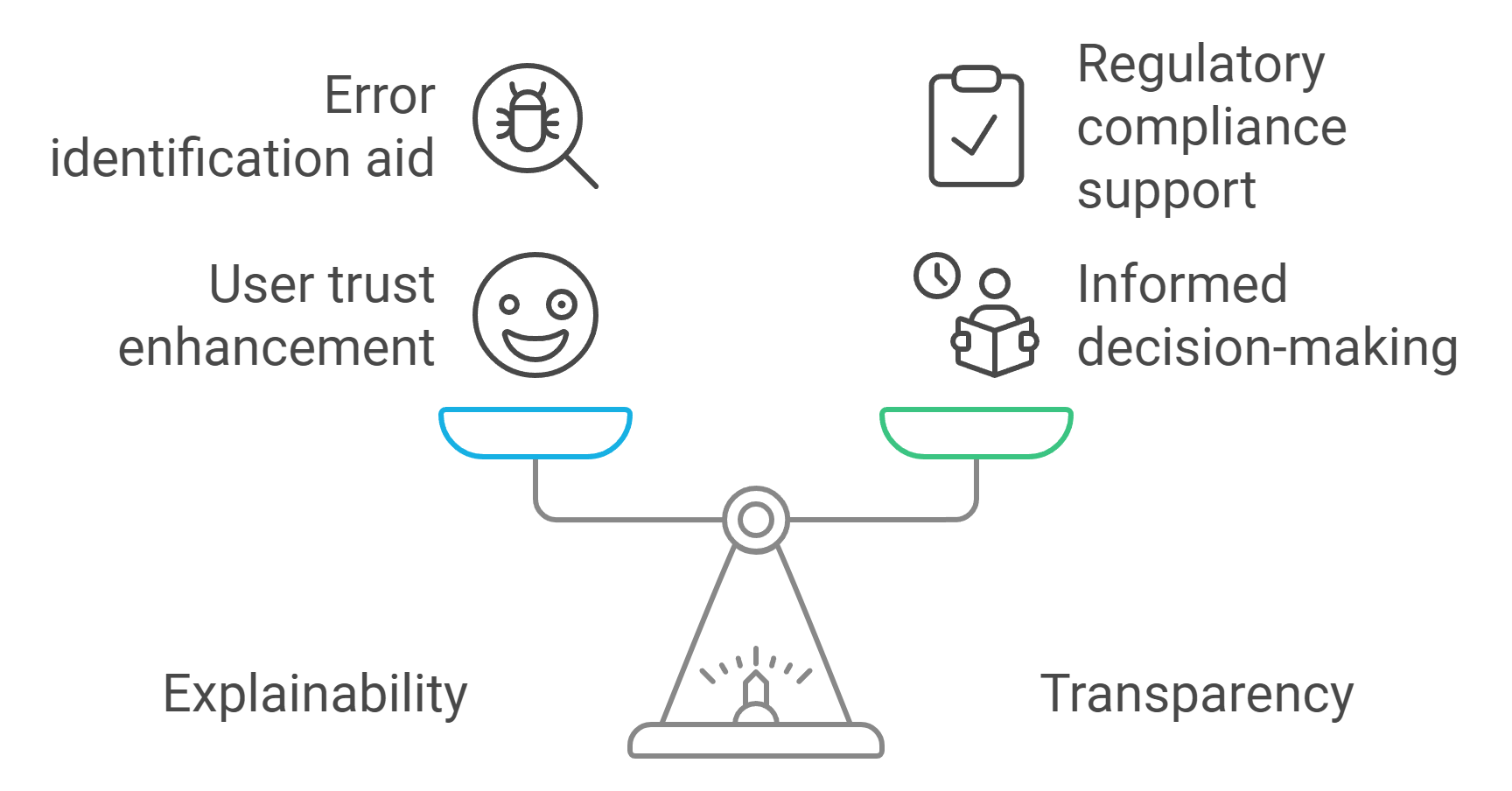
Explainability is a cornerstone of the EU AI Act. You must design your autonomous systems so users can understand how they work. This involves creating clear and accessible explanations of your system's decision-making processes. For instance, if your system uses machine learning algorithms, provide a simplified overview of how it analyzes data and reaches conclusions.
Explainability helps users trust your technology. When people understand how your system operates, they feel more confident using it. Moreover, explainable systems make it easier to identify and correct errors, enhancing overall reliability.
Meeting EU standards for transparency
Transparency goes beyond explainability. The EU AI Act mandates that you disclose specific details about your autonomous systems. These disclosures should cover the system's purpose, functionality, and limitations. For example, if your system assists with medical diagnoses, you must clarify its role and any potential risks involved.
Meeting these transparency standards ensures that users can make informed decisions. It also facilitates regulatory oversight, helping authorities verify that your system complies with the law. By prioritizing transparency, you demonstrate your commitment to ethical and responsible AI development.
Implementing human oversight mechanisms
Balancing automation with human control
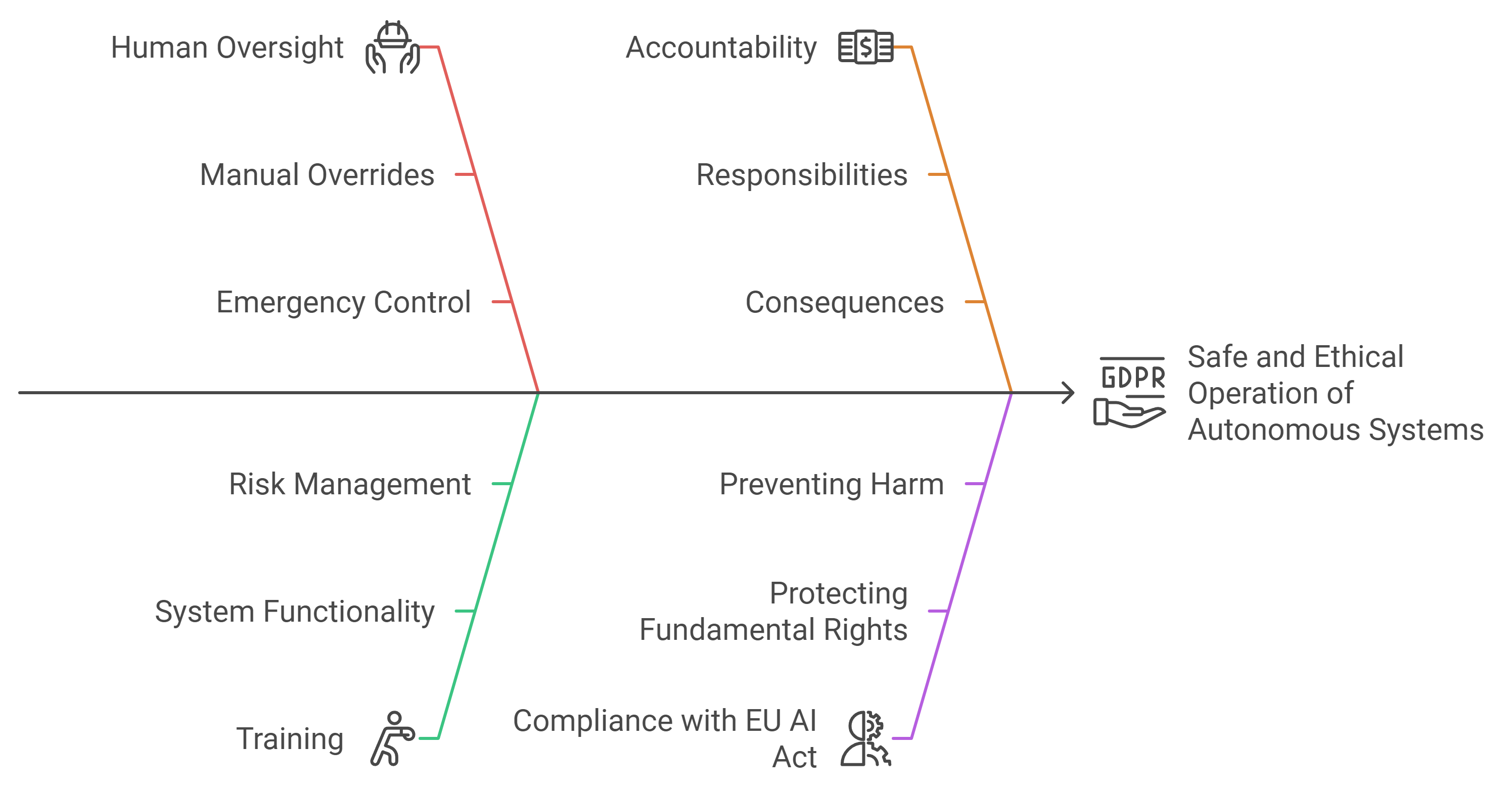
Human oversight is essential for the safe and ethical operation of autonomous systems. The EU AI Act emphasizes the need for mechanisms that allow humans to intervene when necessary. You should design your systems to enable manual overrides or adjustments. For example, in autonomous vehicles, drivers should have the ability to take control in emergencies.
Balancing automation with human control ensures that your systems do not operate unchecked. This approach reduces the risk of errors and enhances user safety. It also aligns with the EU AI Act's focus on protecting fundamental rights and preventing harm.
Training and accountability for operators
Operators play a crucial role in the effective use of autonomous systems. You must provide comprehensive training to ensure they understand how to manage and oversee your technology. This training should cover system functionality, potential risks, and intervention protocols.
Accountability is equally important. Operators should know their responsibilities and the consequences of failing to fulfill them. Clear accountability structures help maintain high standards of operation and compliance. By investing in training and accountability, you support the responsible deployment of your autonomous systems.
Impacts of the EU AI Act on Innovation, Industry, and Global AI Governance
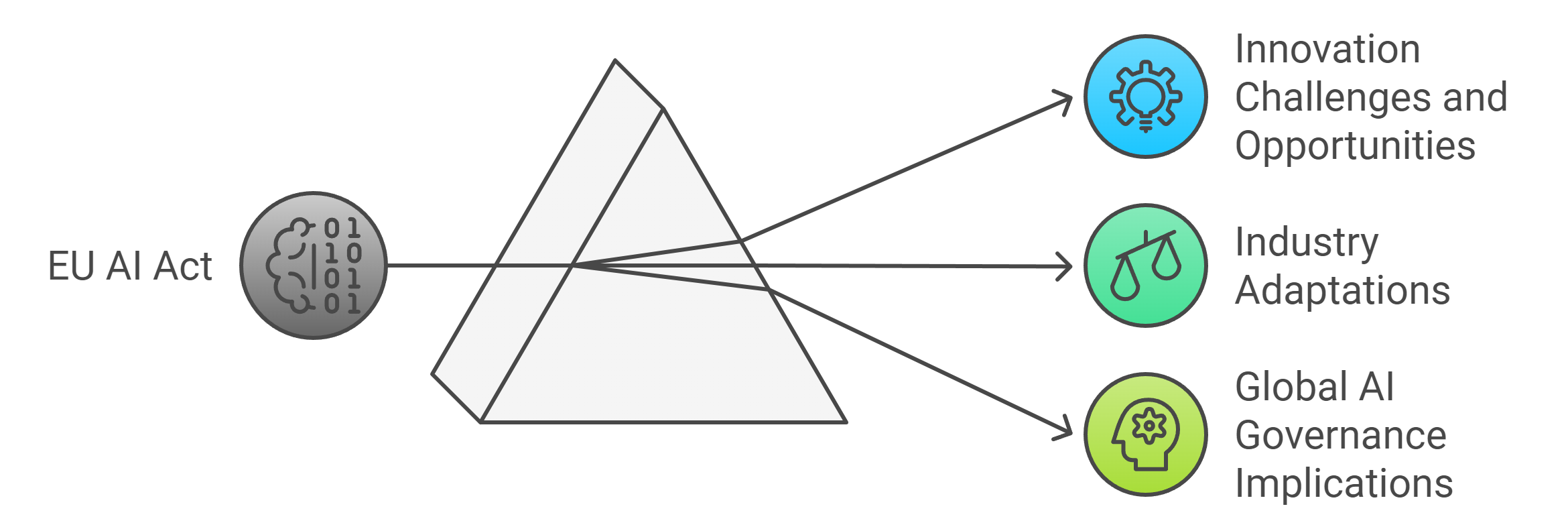
Challenges and opportunities for innovation
The EU AI Act presents both challenges and opportunities for innovation. As a developer or business leader, you must navigate a regulatory landscape that demands compliance while fostering creativity. This balance can feel daunting, but it also opens doors for ethical and responsible advancements in autonomous systems.
Balancing regulatory compliance with technological advancement
You need to align your innovations with the Act’s requirements without stifling creativity. The risk-based framework ensures that high-risk AI systems undergo rigorous scrutiny, which might initially seem restrictive. However, this approach also encourages you to design safer and more reliable technologies. By integrating compliance into your development process, you can create systems that not only meet legal standards but also gain user trust.
Michael Barelli, an expert from AI and Partners, highlights the importance of a robust control framework. He compares the need for impact assessments under the EU AI Act to the data protection impact assessments required by GDPR. This proactive approach helps you identify potential risks early, allowing you to address them without compromising innovation.
Encouraging ethical innovation in autonomous systems
The Act’s emphasis on transparency, safety, and fundamental rights pushes you to think beyond functionality. It challenges you to innovate ethically, ensuring your systems respect privacy and avoid discrimination. Ethical innovation not only aligns with the Act but also enhances your reputation in a market increasingly focused on responsible AI.
The introduction of AI regulatory sandboxes offers a unique opportunity. These controlled environments allow you to test and refine your technologies while ensuring compliance. By leveraging these tools, you can experiment with new ideas without fear of violating regulations.
Industry adaptations to the EU AI Act
The EU AI Act compels industries to rethink their approaches to AI development and deployment. As a stakeholder, you must adapt to these changes to remain competitive and compliant.
Changes in design, development, and deployment practices
You will need to incorporate risk assessments, transparency measures, and human oversight mechanisms into your workflows. These requirements might lead to longer development cycles, but they also result in more robust and trustworthy systems. For instance, designing for explainability ensures users understand how your systems operate, building confidence in your technology.
The healthcare sector provides a clear example of these adaptations. The Act interacts with existing regulations like the EU MDR/IVDR and GDPR, focusing on patient safety and ethical use. This alignment demonstrates how industries can integrate the Act’s principles into their existing frameworks, setting a precedent for other sectors.
Increased focus on compliance and risk management
Compliance becomes a cornerstone of your operations under the EU AI Act. You must invest in training programs to ensure your team understands the regulatory requirements. Regular audits and updates to your systems help maintain compliance and address emerging risks.
Risk management also takes center stage. By conducting thorough assessments, you can identify potential issues before they escalate. This proactive approach not only protects users but also minimizes the likelihood of penalties or reputational damage.
Broader implications for global AI governance
The EU AI Act extends its influence beyond Europe, shaping the global AI governance landscape. As a participant in this ecosystem, you must recognize its broader implications and prepare to align with international standards.
The EU's leadership in setting international AI standards
The Act positions the European Union as a leader in ethical AI governance. Its comprehensive framework serves as a model for other regions, encouraging them to adopt similar standards. This leadership fosters a global dialogue on responsible AI, paving the way for harmonized regulations.
"The EU AI Act is a watershed moment in the global AI governance and regulatory landscape," as noted by experts. Its impact reaches far beyond Europe, influencing companies and policymakers worldwide.
By aligning your practices with the Act, you not only comply with European regulations but also prepare for potential global standards. This foresight gives you a competitive edge in an increasingly interconnected market.
Potential for regulatory harmonization across regions
The Act’s principles of transparency, safety, and ethical use resonate globally. As more countries adopt similar frameworks, you benefit from a more predictable regulatory environment. This harmonization reduces the complexity of operating across borders, allowing you to focus on innovation.
However, achieving this alignment requires continuous engagement. You must stay informed about regulatory developments and contribute to the global conversation on AI governance. By doing so, you help shape a future where innovation and ethics coexist.
The EU AI Act marks a pivotal moment in the regulation of autonomous systems and AI technologies. You must adapt to its requirements to ensure compliance while driving innovation. By prioritizing ethical and transparent practices, you can align with the Act and contribute to the progress of autonomous systems. Its global influence underscores the need for international collaboration, as the Act sets a benchmark for responsible AI governance. This framework not only shapes the future of AI but also fosters trust and accountability on a global scale.
