Secret Ingredients of Data Governance with George Firican
To foster effective data governance, organizations must prioritize three artifacts—the business glossary, data dictionary, and data catalog—similar to having the right components to craft a perfect sandwich.
Imagine you're in a bustling sandwich shop, trying to order your favorite meal, but the menu isn’t clear. Sound familiar? Just like a well-defined sandwich can create a delightful meal, a well-organized data governance structure can foster a thriving business environment. In this post, we’ll navigate through the three must-have artifacts of data governance: the business glossary, the data dictionary, and the data catalog, using the humble sandwich as our guide.
Introduction to the Sandwich Analogy
Imagine this: you walk into your favorite deli, ready to order a sandwich. You have options—turkey, ham, or perhaps a classic grilled cheese. But hold on! Have you ever wondered what exactly defines a sandwich? This might seem trivial, but it’s a perfect analogy to explore the complexities of data governance.
The Sandwich Metaphor
In the world of data governance, the *sandwich* represents the building blocks of organizing information. Just as a sandwich is made up of layers—bread, fillings, sauces—data governance involves multiple layers of policies, procedures, and tools. But what happens when the definition of your “sandwich” differs from someone else’s? This leads us to the crux of the matter. Misinterpretations can arise from differing experiences, much like how you might categorize a grilled cheese as a sandwich while a purist would argue otherwise.
Defining Clarity in Data
When we make a sandwich, clarity is crucial. You need to know what ingredients you want. Similarly, clarity is vital in data governance. If your team lacks a common understanding of terms, confusion will reign. If I asked you, “What’s a data dictionary?” you might have a different version compared to your colleague. This discrepancy can lead to misunderstandings, making it hard to achieve cohesive communication in your organization.
Establishing a Common Ground
Start with definitions: Create a business glossary to document your terms.
Define roles: Clarify who manages what data. Just like knowing who made your sandwich can improve its quality, understanding data stewardship enhances accountability.
Emphasis on communication: Make sure everyone is on the same page. Regular discussions help unify understanding, just like discussing toppings before building that perfect sandwich.
Are you starting to see how your lunch order connects with data governance? It's more than just food—it's about shared understanding and clear definitions.
The Role of Clarity in Ordering
Think back to your last food order. Was there confusion with the waiter? Maybe they didn’t catch your request for extra pickles. This small misunderstanding can lead to disappointment. The same principle applies to data! If your team misinterprets data definitions, it can derail projects. Businesses can lose valuable insights. Clear communication ensures everyone leaves satisfied, whether it’s at a restaurant or in a meeting.
Engaging Personal Experiences
Can you recall a time you ordered a familiar dish only to be surprised by its preparation? Perhaps you thought you were ordering a simple burger, yet what arrived was a gourmet creation! These situations teach a valuable lesson. Expectations versus reality are at play, which perfectly mirrors your data experiences. A well-defined governance strategy can prevent such surprises.
The takeaway here is simple; just as you might use a menu to clarify what you’re ordering, established documentation within your organization can prevent misunderstandings in data handling. Imagine how much smoother your processes would be with a structured approach to metadata. You’d know exactly what to expect—just like knowing the ingredients of your sandwich!
The sandwich analogy helps us grasp a critical idea: assumptions based on experience can lead to misinterpretations, both in food and data. - George Firican
So, next time you're enjoying a multi-layered sandwich, take a moment to think about the layers of data governance. Establishing clear definitions can enhance understanding and bring satisfaction to your organizational “menu.”
What is a Business Glossary?
A business glossary is more than just a list of terms. It's a critical tool that organizations use to ensure everyone speaks the same language. You might be wondering, “Why does this even matter?” The answer is simple: clarity. A well-crafted business glossary enhances understanding, fosters communication, and ignites collaboration across teams.
Definition and Purpose
Put simply, a business glossary is a reference document that defines key business terms and concepts within an organization. It serves several purposes, including:
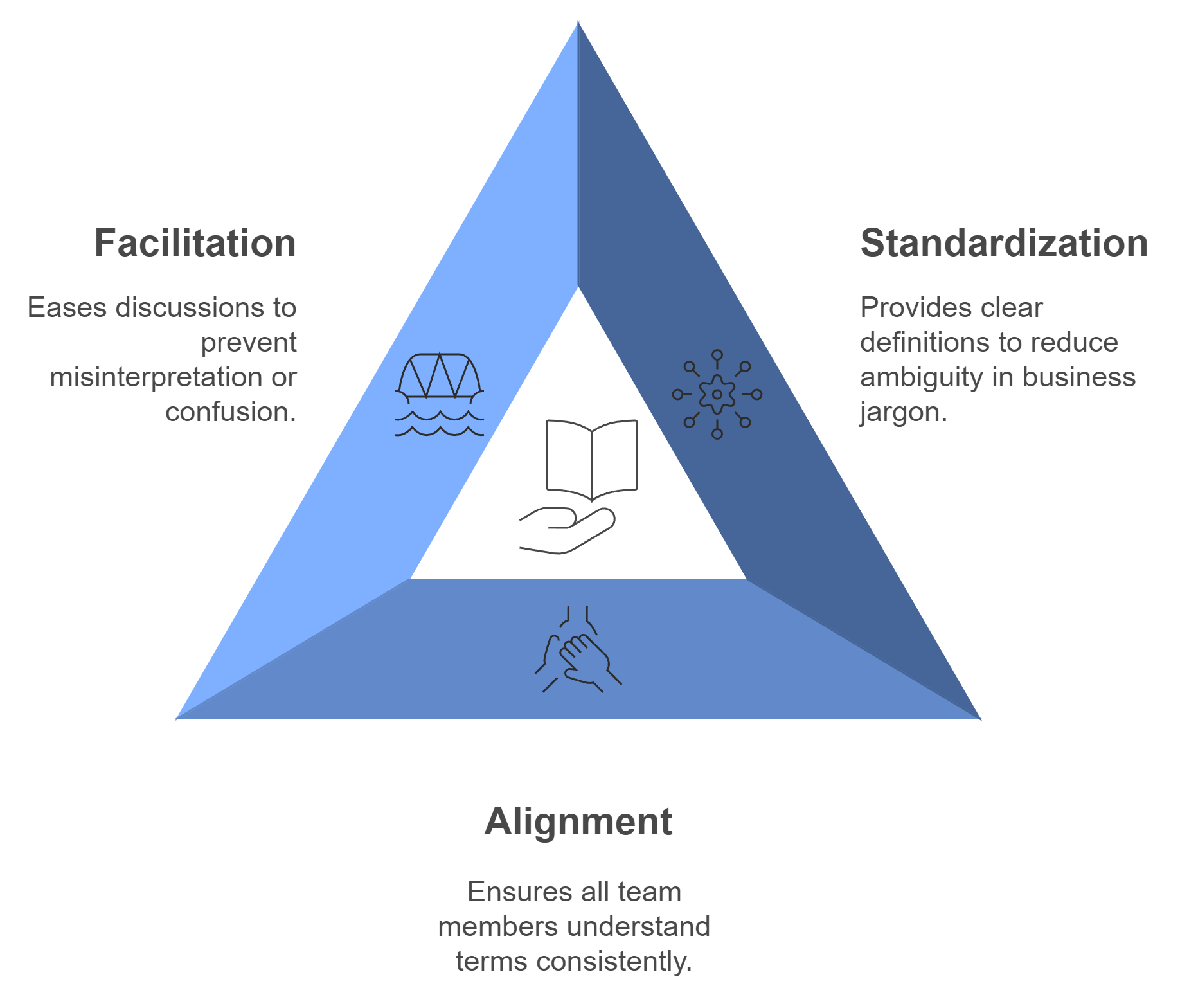
Standardization: By providing clear definitions, it reduces the ambiguity that often accompanies business jargon.
Alignment: A business glossary ensures that all team members, regardless of their role, understand the same terms in the same way.
Facilitation: It eases discussions around topics that might otherwise lead to misinterpretation or confusion.
Imagine your team discussing 'sales metrics.' If one person thinks it refers to revenue and another sees it as customer acquisition, confusion reigns. A business glossary wipes away this uncertainty.
Clarifying Data Terms
Data can be tricky. With so many terms to keep track of, it's easy to get lost. A business glossary acts as a friendly guide. It helps to clarify data terms and ensures consistency across your organization. Suppose you have several teams analyzing customer data. Without a shared understanding of terms like “customer lifetime value” or “churn rate,” they might draw different conclusions. Would you trust those insights? Probably not!
By establishing a business glossary, you provide a foundation for unified data discussions. This creates an informed environment where all team members can contribute intelligently, knowing they’re on the same page.
Real-Life Confusion Examples
Consider a company where the marketing team and the sales team refer to the term “lead” in different ways. For marketing, a lead might simply be someone who filled out a web form. For sales, it could mean a qualified prospect ready to make a purchase. The disconnect can lead to wasted time and missed opportunities.
In another instance, if HR uses “employee engagement” to mean surveys completed while the management team thinks of it as productivity rates, you could face serious reporting issues. Without a business glossary, these misunderstandings fester and expand, creating large-scale operational inefficiency.
Attributes to Include in a Business Glossary
What should you include in your business glossary? Here are some key attributes:
Term: The specific word or phrase.
Definition: A precise explanation of what the term means within your organization.
Synonyms: Other terms that might be used interchangeably.
Ownership: Identify who is responsible for the term’s accuracy (data stewards).
Context: Situations or examples where the term is frequently used.
When you implement these attributes, you build a comprehensive resource. One that not only defines terms but provides a clear context for their use.
Concluding Thoughts
A business glossary is invaluable to your organization. It smoothens the rough edges of communication. The importance of establishing shared definitions can't be overstated. It promotes clarity and improves decision-making. So, are you ready to create one?
Don’t underestimate its power. Embedding a glossary into your organization’s culture is a step toward a more data-informed and collaborative workplace.
Exploring the Data Dictionary
What Is a Data Dictionary?
A data dictionary is like a centralized repository of information about the data in an organization. Think of it as a library where every book (data element) has its own detailed description. This allows users to understand how data is structured, its format, and its purpose. Without it, navigating a sea of data can feel overwhelming and chaotic.
The role of a data dictionary in data architecture is crucial. It helps define not only what data exists but also how it is used. When everyone in your organization shares the same understanding, decisions become easier and more aligned.
Key Components of a Data Dictionary
So, what exactly goes into this valuable artifact? A data dictionary typically includes:
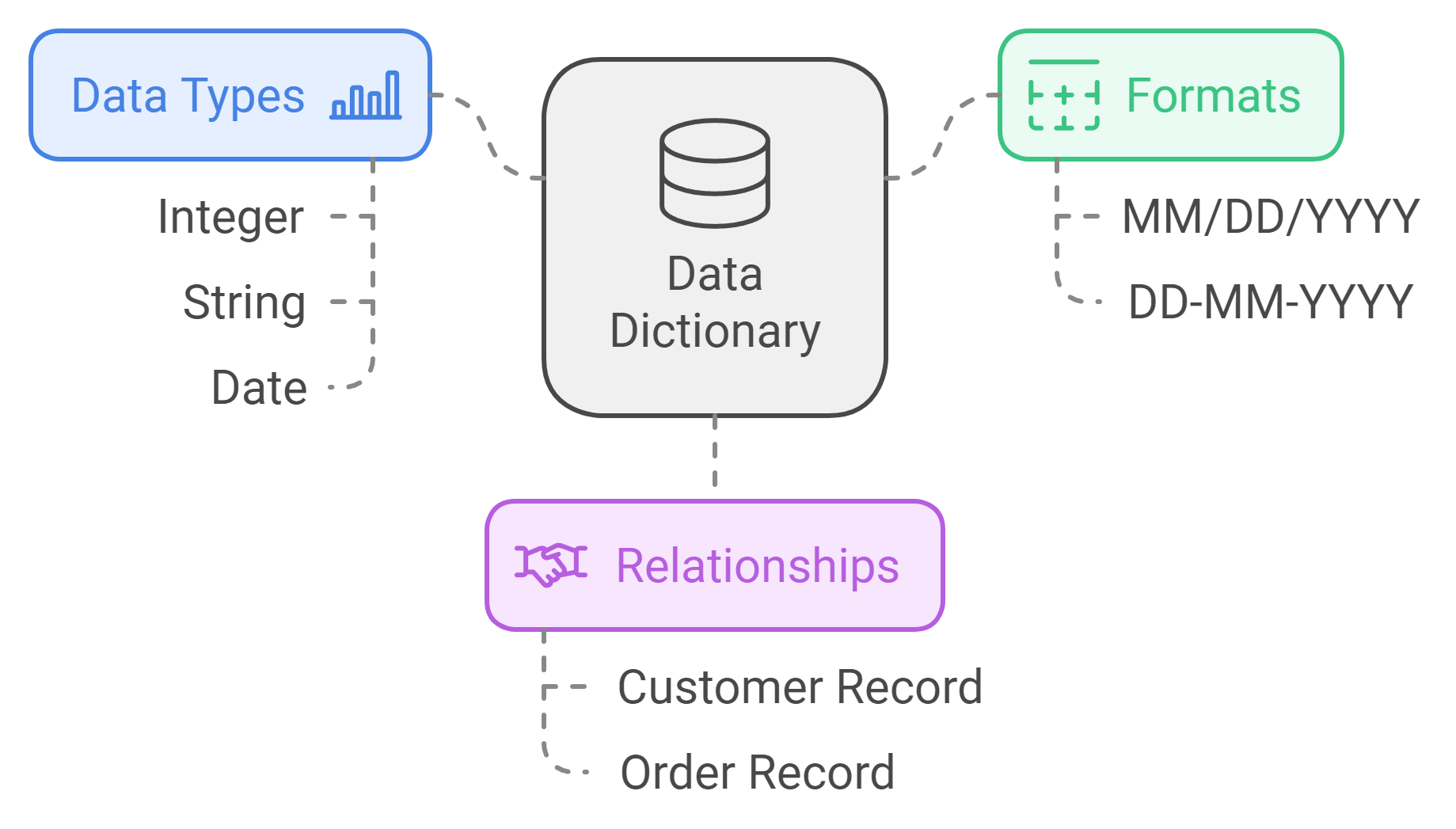
Data Types: These specify the kind of data you are storing, such as integer, string, or date. Understanding these classifications is fundamental.
Formats: This describes how data appears. For example, a date can be in the format MM/DD/YYYY or DD-MM-YYYY. Consistency in format simplifies data handling.
Relationships: Data often links to other data. For instance, a customer record might relate to an order record. Identifying these relationships is key to comprehending data flow.
The Importance of Standardization
Have you ever tried using a tool without proper instructions? Frustrating, right? That’s what happens when data structures aren't standardized. A data dictionary provides this necessary structure.
Having a standardized data structure ensures that everyone is on the same page. It fosters consistency, clarity, and accuracy. When you define terms, formats, and relationships clearly, you minimize errors. You might even avoid catastrophic misunderstandings in data interpretation.
Common Pitfalls Without a Data Dictionary
Imagine driving a car without knowing how to read the traffic signs. That’s similar to navigating data without a data dictionary. Here are some common pitfalls you might encounter:
Miscommunication: When terms are undefined, everyone might have a different understanding. This can lead to conflicting insights and decisions.
Data Inconsistency: Without clear definitions, you risk having different formats for the same data type. For instance, what if one department uses “$1,000” while another writes “1000.00”? Confusion, right?
Increased Errors: Users may accidentally input the wrong data or misinterpret it. Errors can cascade, affecting the overall quality of your data.
The Role of a Data Catalog
What is a Data Catalog?
A data catalog is a centralized repository that acts like a library for an organization's data assets. It stores metadata, which is data about data. Think of it as a map that guides you through the vastness of all your data sources. Just as a library catalog helps you find a book you're looking for, a data catalog helps you find the specific data you need for your projects.

How Does a Data Catalog Organize Your Data?
Imagine walking into a huge storage room filled with boxes, each containing valuable information. Without a proper organization system, finding anything would be a nightmare. This is where a data catalog shines. It organizes your organization's data stores by:
Classifying Data: It categorizes data based on various attributes, making it easy to locate.
Providing Metadata: The catalog includes detailed descriptions, lineage, and usage rights of datasets, similar to product descriptions on an e-commerce site.
Facilitating Data Discovery: You can easily search for datasets, understand their context, and assess their relevance before using them.
With a well-structured data catalog, accessing the right data becomes straightforward. You can move quickly from one dataset to another, optimizing your workflow.
Consumer Behavior and Data-Driven Decision-Making
Have you ever wondered how companies seem to know what you want before you even think of it? This intuitiveness often stems from analyzing data. A data catalog plays a crucial role in this process by providing a comprehensive view of available data. When businesses leverage their data effectively, they can:
Enhance Customer Experiences: By understanding consumer preferences, organizations can tailor their products and services to meet specific needs.
Predict Trends: Listening to the pulse of data helps identify emerging trends early, allowing businesses to stay ahead of the competition.
Make Informed Decisions: Access to accurate data enables companies to make decisions based not on guesswork, but on tangible evidence.
Thus, a well-maintained data catalog brings real-time, actionable insights that can significantly impact consumer behavior and enhance overall effectiveness in data-driven decision-making.
Operational Efficiencies Gained from Data Catalogs
Operational efficiency in any organization can literally define its success. Data catalogs are a game-changer in this regard. Here’s how they can boost operational efficiencies:
Streamline Processes: By simplifying data access, teams spend less time searching for information and more time analyzing it.
Reduce Redundancies: A central place for data minimizes duplicated efforts across teams, promoting consistency and collaboration.
Enhance Data Quality: Regular updates and data governance practices foster a culture of data quality, which is crucial for accurate analysis.
So, if your organization is still wrestling with data chaos, implementing a data catalog could be the solution you need. And let’s face it—navigating data without one is like trying to find a needle in a haystack!
“A well-structured data catalog can act as a beacon, guiding organizations through the murky waters of data management.”
With these insights, it's clear that the role of a data catalog extends beyond mere organization. It empowers teams to harness the potential of their data, unlocking opportunities and fostering innovation.
The Interconnection of the Artifacts
Understanding the relationship between the business glossary, data dictionary, and data catalog is essential for any organization aiming to thrive in today's data-driven landscape. These artifacts do not exist in isolation; they are interconnected and work together like pieces of a puzzle. So, let's break it down step by step.
1. The Artifacts Explained
Business Glossary: This is your go-to source for definitions and explanations of business terms. Imagine it as a dictionary but specific to your organization’s context. It ensures everyone is on the same page.
Data Dictionary: Think of this as the technical counterpart to the business glossary. It details specific data elements, their attributes, types, and relationships. It provides the technical specifications that complement the business terminology.
Data Catalog: Picture this as an organized "store" of all your datasets. Just like how you browse through categories on Amazon, a data catalog helps users discover and access data effectively.
When you look closely, it’s clear: these artifacts are not just databases or lists. They are frameworks that facilitate understanding and usage of data throughout your organization.
2. How They Work Together
Let me ask you a question: Have you ever tried to find a book without knowing its title? It can be frustrating, right? The same goes for data. Without the right tools, identifying and using data can feel overwhelming.
Here are a few examples of how these artifacts function in synergy:
With a business glossary, stakeholders can familiarize themselves with terminology. When they delve into the data dictionary for technical specifics, they can seamlessly translate that understanding into practical data usage.
The data catalog serves as a bridge by linking back to both the glossary and dictionary. When you discover a dataset, the catalog will often provide links to its definitions and specifications, making it easier to comprehend the context and usage.
For instance, if a marketing analyst wants to assess customer demographics, the data catalog helps them locate relevant datasets quickly. They can then cross-reference the data dictionary for data field details and, if needed, refer back to the glossary for term definitions
This interconnectedness enhances your organization's data practices. It encourages not just data usage but informed decision-making.
3. Collaboration is Key
Ever wonder why some teams excel at data management while others struggle? The answer often lies in collaboration. Maintaining these artifacts isn't a siloed task; it requires teamwork.
Here’s why collaboration is essential:
Consistency: When multiple teams contribute to the glossary and dictionary, they help ensure consistency in definitions and usage. This prevents confusion and miscommunication.
Feedback Loop: Stakeholders should feel empowered to provide feedback. This participatory approach can lead to updates in the glossary or catalog that better reflect the organization's evolving needs.
Enhanced Data Literacy: By collaborating across various departments, you create a culture of learning. Your team members will understand the importance of these artifacts and how to use them effectively, increasing overall data literacy.
Think of it this way: just like a well-oiled machine, collaboration ensures that all parts — the glossary, dictionary, and catalog — function smoothly together. Without it, you risk creating gaps in understanding that can hinder your data-driven efforts.
Combining these artifacts with engaged collaboration paves the way for a strong foundation in data practices. It fosters an environment where data can truly shine as a critical resource for your organization.
Case Study: A Sandwich Shop's Data Dilemmas
Imagining a Small Sandwich Shop
Picture this: a cozy little sandwich shop nestled in the corner of a bustling street. The aroma of freshly baked bread fills the air. Customers are ordering their favorite subs and wraps. Sounds lovely, right? But what if I told you that this charming shop is missing a critical element for success—proper data governance.
Without data governance, the shop struggles to understand what's truly happening within its walls. How many sandwiches are sold daily? What ingredients are running low? Which toppings are the most popular? These questions linger in the owner's mind, like an unfinished order.
The Challenges Faced
Imagine each day is chaotic. Sales fluctuate without a clear pattern. The owner tries to guess what to prepare based on memory and assumptions. This can lead to:
Overstocked ingredients: If they think they need 20 pounds of turkey but only sell 10, it leads to waste.
Mismatched expectations: Customers might want a special yesterday’s sandwich, but it’s out of stock today.
Poor planning: They may not realize that Mondays are busier than Wednesdays, leaving staff overwhelmed on one day and twiddling their thumbs on another.
Each of these challenges compounds over time. They affect customer satisfaction, staff morale, and ultimately, profits. Like driving a car without a dashboard, the owner has no visibility into how the shop is performing.
How to Improve: Business Glossary, Data Dictionary, and Data Catalog
Now, what if this sandwich shop had a robust data strategy? What if they established three essential data governance tools: a business glossary, data dictionary, and data catalog? Let's explore how these could solve many of their challenges.
1. Business Glossary
A business glossary defines key terms and concepts used in the shop. For example:
What is a “special sandwich”? This could vary from day to day.
What is “inventory count”? It’s a different approach for some ingredients versus others.
With a glossary, everyone—from the chef to the cashier—knows precisely what is meant when discussing menu items. This shared understanding reduces confusion, ensuring smoother operations.
2. Data Dictionary
A data dictionary details the specifics of their data elements. Here, they’d document:
The price of each sandwich
Ingredient types (e.g., gluten-free bread, organic lettuce)
Sales channels(walk-in, online, delivery)
This information guides staff in how to manage inventory and handle sales data effectively. It acts like a map, leading everyone toward smarter decisions.
3. Data Catalog
Finally, a data catalog serves as an organized repository. Think of it as the sandwich shop’s menu but for internal data. It captures:
Select customer reviews about different sandwiches
Sales trends over specific times of the year
Links to data dictionaries where more detail can be found
This catalog makes data more accessible for every employee. Just like a customer browsing the menu, staff can easily find the information they need to make informed choices. With clarity in data, the sandwich shop can turn chaos into harmony.
Imagine the restaurant thriving, making data-informed decisions that boost customer satisfaction and profitability. Isn't that a delightful thought? With the right data governance practices in place, even a small sandwich shop can serve up success one tasty bite at a time.
Key Takeaways and Conclusion
As we wrap up this exploration of essential artifacts in data-driven organizations, it’s vital to reflect on three crucial elements that have emerged. These artifacts—business glossaries, data dictionaries, and data catalogs—form a strong foundation for effective data management and communication within your workplace. They are indispensable tools for ensuring everyone on your team is on the same page.
The Importance of the Three Artifacts
Organizations thrive on collaboration, and a unified understanding of terms is key. By integrating a business glossary, you ensure that all stakeholders can confidently navigate the jargon and terminology specific to your organization. This artifact serves as a reference point, reducing misunderstandings and enhancing clarity.
Next, consider the role of the data dictionary. This tool plays a critical part in documenting the specifications of data elements. It’s more than just a list; it’s a guide that helps you understand the attributes of data needed for processes like ETL (Extract, Transform, Load). When you have insight into what data means and how it should be used, you set the stage for successful projects.
Lastly, a well-structured data catalog provides easy access to all your organization’s data stores. This is particularly useful for teams that need to find and utilize data quickly. It’s akin to shopping on Amazon, where you can explore products with detailed descriptions. In the same vein, your data catalog helps users to effectively discover and evaluate information, making your data more accessible and useful.
The Sandwich Analogy
Throughout our discussion, the sandwich analogy has provided a relatable way to understand these artifacts' significance. Just as a sandwich comprises layers that come together to create a satisfying meal, these artifacts build upon one another to form a coherent data governance structure. Can you imagine categorizing a grilled cheese as a sandwich based solely on your personal experience? George’s playful challenge reminds you that definitions vary and that you should always seek clarity in your terminology.
This is especially true in data management, where assumptions can lead to significant misinterpretations. The sandwich analogy illustrates the necessity of having a shared definition of terms, ensuring that everyone understands what is meant, regardless of their background or prior experiences.
A Call to Action for Data Professionals
As a data professional, you have the power to advocate for these essential structures within your organization. Embrace the role of a data steward who champion communication and understanding, ensuring your colleagues utilize these artifacts for better data governance and literacy. Talk to your team about the importance of establishing a business glossary and a data dictionary. Fight for the integration of a robust data catalog.
Remember that data literacy leads to stronger data culture, and fostering a collaborative environment can shatter barriers in data understanding. It’s not just about managing data; it’s about creating a workplace where everyone feels empowered to use it effectively. You have the knowledge; now it’s time to share it!
In conclusion, as you move forward in your data journey, keep in mind the invaluable resources that a comprehensive understanding of these artifacts presents. Like a sandwich, these elements layer upon one another, creating a unified approach to tackling data challenges. Whether you’re defining terms, documenting data elements, or cataloging resources, you are paving the way for a thriving data ecosystem in your organization.
